The history of mankind is a continuous struggle for territorial domination. Great empires either appeared on the political map of the world or disappeared from it. Some of them were destined to leave an indelible mark.
Persian Empire (Achaemenid Empire, 550 - 330 BC)
Cyrus II is considered to be the founder of the Persian Empire. He began his conquests in 550 BC. e. from the subjugation of Media, after which Armenia, Parthia, Cappadocia and the Lydian kingdom were conquered. Did not become an obstacle to the expansion of the empire of Cyrus and Babylon, whose powerful walls fell in 539 BC. e.
Conquering neighboring territories, the Persians tried not to destroy the conquered cities, but, if possible, to preserve them. Cyrus restored the captured Jerusalem, as well as many Phoenician cities, by facilitating the return of the Jews from the Babylonian captivity.
The Persian Empire under Cyrus stretched its possessions from Central Asia to the Aegean Sea. Only Egypt remained unconquered. The country of the pharaohs submitted to the heir of Cyrus Cambyses II. However, the empire reached its heyday under Darius I, who switched from conquests to domestic politics. In particular, the king divided the empire into 20 satrapies, which completely coincided with the territories of the occupied states.
In 330 B.C. e. the weakening Persian Empire fell under the onslaught of the troops of Alexander the Great.
Roman Empire (27 BC - 476)

Ancient Rome was the first state in which the ruler received the title of emperor. Starting with Octavian Augustus, the 500-year history of the Roman Empire had the most direct impact on European civilization, and also left a cultural mark in the countries of North Africa and the Middle East.
The uniqueness of Ancient Rome is that it was the only state whose possessions included the entire Mediterranean coast.
During the heyday of the Roman Empire, its territories stretched from the British Isles to the Persian Gulf. According to historians, by the year 117 the population of the empire reached 88 million people, which was approximately 25% of the total number of inhabitants of the planet.
Architecture, construction, art, law, economics, military affairs, the principles of the state structure of Ancient Rome - this is what the foundation of the entire European civilization is based on. It was in Imperial Rome that Christianity assumed the status of the state religion and began to spread throughout the world.
Byzantine Empire (395 - 1453)

The Byzantine Empire has no equal in the length of its history. Originating at the end of antiquity, it existed until the end of the European Middle Ages. For more than a thousand years, Byzantium has been a kind of link between the civilizations of the East and the West, influencing both the states of Europe and Asia Minor.
But if the Western European and Middle Eastern countries inherited the richest material culture of Byzantium, then the Old Russian state turned out to be the successor to its spirituality. Constantinople fell, but the Orthodox world found its new capital in Moscow.
Located at the crossroads of trade routes, rich Byzantium was a coveted land for neighboring states. Having reached its maximum borders in the first centuries after the collapse of the Roman Empire, then it was forced to defend its possessions. In 1453, Byzantium could not resist a more powerful enemy - the Ottoman Empire. With the capture of Constantinople, the road to Europe was opened for the Turks.
Arab Caliphate (632-1258)

As a result of the Muslim conquests in the 7th-9th centuries, the theocratic Islamic state of the Arab Caliphate arose on the territory of the entire Middle East region, as well as certain regions of the Transcaucasus, Central Asia, North Africa and Spain. The period of the Caliphate went down in history under the name "Golden Age of Islam", as the time of the highest flowering of Islamic science and culture.
One of the caliphs of the Arab state, Umar I, purposefully secured the character of a militant church for the Caliphate, encouraging religious zeal in his subordinates and forbidding them to own land property in the conquered countries. Umar motivated this by the fact that "the interests of the landowner attract him more to peaceful activities than to war."
In 1036, the invasion of the Seljuk Turks turned out to be disastrous for the Caliphate, but the Mongols completed the defeat of the Islamic state.
Caliph An-Nasir, wishing to expand his possessions, turned to Genghis Khan for help, and without knowing it opened the way for the ruin of the Muslim East to the many thousands of Mongol hordes.
Mongol Empire (1206–1368)

The Mongol Empire is the largest state formation in history in terms of territory.
In the period of its power - by the end of the XIII century, the empire stretched from the Sea of Japan to the banks of the Danube. The total area of possessions of the Mongols reached 38 million square meters. km.
Given the vast size of the empire, managing it from the capital, Karakorum, was almost impossible. It is no coincidence that after the death of Genghis Khan in 1227, the process of gradual division of the conquered territories into separate uluses began, the most significant of which was the Golden Horde.
The economic policy of the Mongols in the occupied lands was primitive: its essence was reduced to the taxation of tribute to the conquered peoples. All collected went to support the needs of a huge army, according to some sources, reaching half a million people. The Mongol cavalry was the most deadly weapon of the Genghisides, which few armies managed to resist.
The inter-dynastic strife ruined the empire - it was they who stopped the expansion of the Mongols to the West. This was soon followed by the loss of the conquered territories and the capture of the Karakorum by the troops of the Ming Dynasty.
Holy Roman Empire (962-1806)
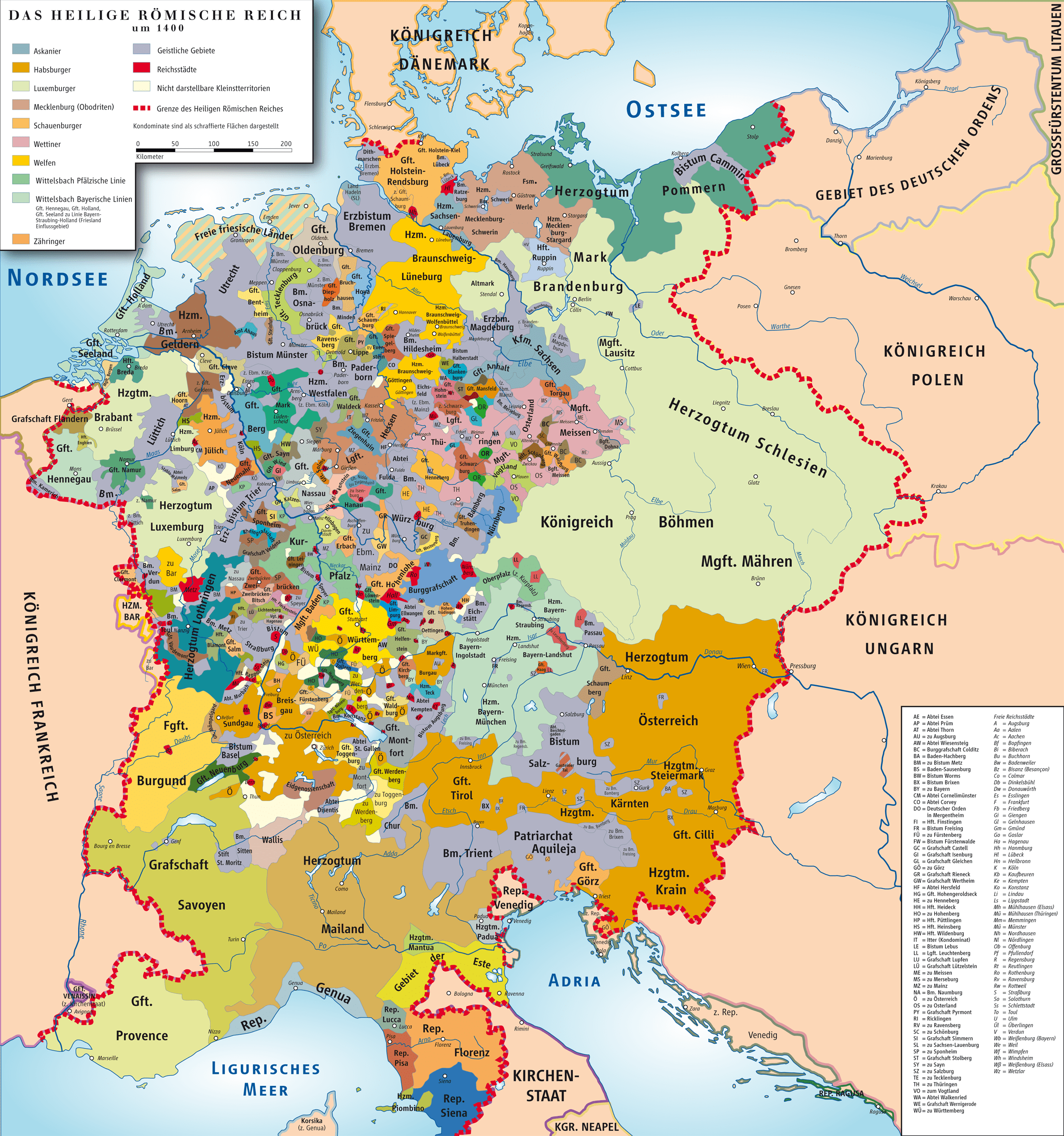
The Holy Roman Empire is an interstate entity that existed in Europe from 962 to 1806. The core of the empire was Germany, which was joined by the Czech Republic, Italy, the Netherlands, and some regions of France during the period of the highest prosperity of the state.
For almost the entire period of the empire's existence, its structure had the character of a theocratic feudal state, in which emperors claimed supreme power in the Christian world. However, the struggle with the papacy and the desire to possess Italy significantly weakened the central power of the empire.
In the 17th century, Austria and Prussia advanced to leading positions in the Holy Roman Empire. But very soon, the antagonism of two influential members of the empire, which resulted in an aggressive policy, threatened the integrity of their common home. The end of the empire in 1806 was put by the growing France, led by Napoleon.
Ottoman Empire (1299–1922)

In 1299, Osman I created a Turkic state in the Middle East, which was destined to exist for more than 600 years and radically influence the fate of the countries of the Mediterranean and Black Sea regions. The fall of Constantinople in 1453 was the date when the Ottoman Empire finally gained a foothold in Europe.
The period of the highest power of the Ottoman Empire falls on the 16th-17th centuries, but the state achieved the greatest conquests under Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent.
The borders of the empire of Suleiman I stretched from Eritrea in the south to the Commonwealth in the north, from Algiers in the west to the Caspian Sea in the east.
The period from the end of the 16th century to the beginning of the 20th century was marked by bloody military conflicts between the Ottoman Empire and Russia. Territorial disputes between the two states mainly unfolded around the Crimea and Transcaucasia. The First World War put an end to them, as a result of which the Ottoman Empire, divided between the countries of the Entente, ceased to exist.
British Empire (1497–1949)

The British Empire is the largest colonial power both in terms of territory and population.
The empire reached its greatest extent by the 30s of the 20th century: the land area of the United Kingdom, together with the colonies, totaled 34 million 650 thousand square meters. km., which was approximately 22% of the earth's land. The total population of the empire reached 480 million people - every fourth inhabitant of the Earth was a subject of the British crown.
Many factors contributed to the success of British colonial policy: a strong army and navy, developed industry, and the art of diplomacy. The expansion of the empire had a significant impact on world geopolitics. First of all, this is the spread of British technology, trade, language, and forms of government around the world.
The decolonization of Britain took place after the end of World War II. The country, although it was among the victorious states, was on the verge of bankruptcy. Only thanks to an American loan of 3.5 billion dollars, Great Britain was able to overcome the crisis, but at the same time it lost world domination and all its colonies.
Russian Empire (1721–1917)

The history of the Russian Empire dates back to October 22, 1721, after the adoption by Peter I of the title of Emperor of All Russia. From that time until 1905, the monarch who became the head of the state was endowed with absolute fullness of power.
In terms of area, the Russian Empire was second only to the Mongol and British empires - 21,799,825 square meters. km, and was the second (after the British) in terms of population - about 178 million people.
The constant expansion of the territory is a characteristic feature of the Russian Empire. But if the advance to the east was mostly peaceful, then in the west and south Russia had to prove its territorial claims through numerous wars - with Sweden, the Commonwealth, the Ottoman Empire, Persia, the British Empire.
The growth of the Russian Empire has always been viewed with particular caution by the West. The appearance of the so-called "Testament of Peter the Great" - a document fabricated in 1812 by French political circles - contributed to the negative perception of Russia. “The Russian State must establish power over all of Europe,” is one of the key phrases of the Testament, which will haunt the minds of Europeans for a long time to come.
It is in history that answers to many questions of our time can be found. Do you know about the largest empire that ever existed on the planet? TravelAsk will tell about two world giants of the past.
The largest empire by area
The British Empire is the largest state that has ever existed in the history of mankind. Of course, here we are talking not only about the continent, but also colonies on all inhabited continents. Just think: that was even less than a hundred years ago. At different times, the area of Britain was different, but the maximum is 42.75 million square meters. km (of which 8.1 million sq. km are territories in Antarctica). This is two and a half times more than today's territory of Russia. This is 22% sushi. The heyday of the British Empire came in 1918.
The total population of Britain at its peak was about 480 million people (about one-fourth of humanity). That is why English is so widespread. This is a direct legacy of the British Empire.
How the state was born
The British Empire grew over a long period of about 200 years. The 20th century was the culmination of its growth: at that time, the state possessed various territories on all continents. For this, it is called the empire, "over which the sun never sets."
And it all started in the 18th century quite peacefully: with trade and diplomacy, occasionally with colonial conquests.

The empire helped spread British technology, trade, the English language and its form of government around the world. Of course, the basis of power was the navy, which was used everywhere. He ensured freedom of navigation, fought slavery and piracy (slavery was abolished in Britain at the beginning of the 19th century). This made the world a safer place. It turns out that instead of seeking power over vast inland territories for the sake of possessing resources, the empire relied on trade and control over strategically important points. It was this strategy that made the British Empire the most powerful.

The British Empire was very diverse, including territories on all continents, which created a great diversity of cultures. The state included a very heterogeneous population, thanks to which it was able to manage various regions either directly or through local rulers, these are excellent skills for the government. Just think: British power extended to India, Egypt, Canada, New Zealand and many other countries.

When the decolonization of the United Kingdom began, the British tried to introduce parliamentary democracy and the rule of law in the former colonies, but this was far from successful everywhere. The influence of Great Britain on its former territories is still noticeable today: most of the colonies decided that the Commonwealth of Nations replaced the Empire in psychological terms. Members of the Commonwealth are all former dominions and colonies of the state. Today it includes 17 countries, including the Bahamas and others. That is, they in fact recognize the monarch of Great Britain as their monarch, but on the spot his power is represented by the governor general. But it is worth saying that the title of monarch does not imply any political power over the Commonwealth Realms.
Mongol Empire
The second largest (but not powerful) is the Mongol Empire. It was formed as a result of the conquests of Genghis Khan. Its area is 38 million square meters. km: this is slightly less than the area of Britain (and if you consider that Britain owned 8 million square kilometers in Antarctica, then the figure looks even more impressive). The territory of the state stretched from the Danube to the Sea of Japan and from Novgorod to Cambodia. This is the largest continental state in the history of mankind.

The state did not last long: from 1206 to 1368. But this empire influenced the modern world in many ways: it is believed that 8% of the world's population are descendants of Genghis Khan. And this is quite likely: only the eldest son of Temujin had 40 sons.
During its heyday, the Mongol Empire included vast territories of Central Asia, Southern Siberia, Eastern Europe, the Middle East, China and Tibet. It was the largest land empire in the world.
Its rise is astonishing: a group of Mongol tribes, no more than a million in number, managed to conquer empires that were literally hundreds of times larger. How did they achieve this? Thoughtful tactics of action, high mobility, the use of technical and other achievements of the captured peoples, as well as the correct organization of logistics and supplies.
.jpeg)
But here, of course, there could be no talk of any diplomacy. The Mongols completely cut out the cities that did not want to obey them. More than one city was swept off the face of the earth. Moreover, Temujin and his descendants destroyed the great and ancient states: the state of Khorezmshahs, the Chinese Empire, the Baghdad Caliphate, Volga Bulgaria. Modern historians say that up to 50% of the total population died in the occupied territories. Thus, the population of Chinese dynasties was 120 million people, after the invasion of the Mongols, it decreased to 60 million.
The consequences of the invasions of the great khan
The commander Temujin united all the Mongol tribes by 1206 and was proclaimed the great khan over all the tribes, receiving the title "Genghis Khan". He captured northern China, devastated Central Asia, conquered all of Central Asia and Iran, ruining the entire region.

The descendants of Genghis Khan ruled an empire that captured most of Eurasia, including almost the entire Middle East, parts of Eastern Europe, China and Rus'. Despite all the power, the real threat to the dominance of the Mongol Empire was the enmity between its rulers. The empire split into four khanates. The largest fragments of Great Mongolia were the Yuan Empire, the Ulus of Jochi (Golden Horde), the state of the Khulaguids and the Chagatai ulus. They, in turn, also collapsed or were subdued. In the last quarter of the 14th century, the Mongol Empire ceased to exist.
However, despite such a short reign, the Mongol Empire influenced the unification of many regions. So, for example, the eastern and western parts of Russia and the western regions of China remain united to this day, although in different forms of government. Rus' also gained strength: during the Tatar-Mongol yoke, Moscow was granted the status of a tax collector for the Mongols. That is, Russian residents collected tribute and taxes for the Mongols, while the Mongols themselves rarely visited Russian lands. In the end, the Russian people received military power, which allowed Ivan III to overthrow the Mongols under the rule of the Moscow principality.
In our world, nothing lasts forever: after birth and flourishing, sunset inevitably follows. This rule also applies to states. Hundreds of states have been created and collapsed over thousands of years of historical epoch. We will find out which of them existed on Earth for the longest time, until they fell apart for one reason or another. Perhaps some of them did not amaze the world with their grandeur and brilliance, but they were strong with their centuries-old history.
Portuguese Colonial Empire
560 years (1415 -1975)
The prerequisites for the creation of the Portuguese Colonial Empire appeared simultaneously with the beginning of the Great Geographical Discoveries. By 1415, the Portuguese navigators, of course, had not yet reached the shores of America, but they were already actively exploring the African continent, starting to search for a short sea route to India. The Portuguese declared open lands their property, erecting forts and fortresses everywhere.
By its heyday, the Portuguese Colonial Empire had fortifications in West Africa, East and South Asia, India and the Americas. The Portuguese Empire became the first state in history to unite territories on four continents under its flag. Thanks to the trade in spices and jewelry, the Portuguese treasury was bursting with gold and silver, which allowed the state to exist for such a long time.

Napoleonic wars, internal contradictions and external enemies nevertheless undermined the power of the state, and by the beginning of the 20th century there was no trace left of the former greatness of the Portuguese Colonial Empire. Officially, the empire ceased to exist in 1975, when democracy was established in the metropolis.
624 years (1299 AD -1923 AD)
The state, founded by Turkic tribes in 1299, reached its peak in the 17th century. The huge multinational Ottoman Empire stretched from the borders of Austria to the Caspian Sea, owning territories in Europe, Africa, and Asia. Wars with the Russian Empire, the loss in the First World War, internal contradictions and constant Christian uprisings undermined the strength of the Ottoman Empire. In 1923, the monarchy was abolished and the Republic of Turkey established in its place.
Khmer Empire
629 years (802 AD -1431 AD)
Not everyone has heard of the existence of the Khmer Empire, which is one of the oldest state entities in history. The Khmer Empire was formed as a result of the unification of the Khmer tribes living in the 8th century AD. in Indochina. During its highest power, the Khmer Empire included the territories of Cambodia, Thailand, Vietnam and Laos. But its rulers did not calculate the gigantic costs of building temples and palaces, which gradually devastated the treasury. The weakened state in the first half of the 15th century finally finished off the invasion of the Thai tribes that had begun.
Kanem
676 years (700 AD -1376 AD)
Despite the fact that individually African tribes do not pose a danger, united, they can create a strong and warlike state. This is how the Kanem Empire was formed, located for almost 700 years on the territory of modern Libya, Nigeria and Chad.
 Territory of Kanem | commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kanem-Bornu.svg
Territory of Kanem | commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Kanem-Bornu.svg The reason for the fall of a strong empire was internal strife after the death of the last emperor, who had no heirs. Taking advantage of this, various tribes located on the borders invaded the empire from different sides, hastening its fall. The surviving indigenous people were forced to leave the cities and return to a nomadic way of life.
Holy Roman Empire
844 (962 AD - 1806 AD)

The Holy Roman Empire is not the same Roman Empire whose iron legions captured almost the entire world known to ancient Europe. The Holy Roman Empire was not even located in Italy, but on the territory of modern Germany, Austria, Holland, the Czech Republic and part of Italy. The unification of the lands took place in 962, and the new Empire was intended to be a continuation of the Western Roman Empire. The European order and discipline allowed this state to exist for eight and a half centuries, while the complex system of state administration, degraded, weakened the central authority, which led to the decline and collapse of the Holy Roman Empire.
Kingdom of Silla
992 (57 BC - 935 AD)

At the end of the first century BC. on the Korean Peninsula, three kingdoms fought desperately for a place under the sun, one of which - Silla - managed to defeat its enemies, annexed their lands and founded a powerful dynasty that lasted almost a thousand years, which ingloriously disappeared in the fires of civil war.
994 (980 AD -1974 AD)

We often think that before the arrival of European colonizers, Africa was a completely wild area inhabited by primitive tribes. But on the African continent, there was a place for an empire that existed for almost a thousand years! Founded in 802 by the united Ethiopian tribes, the empire did not “hold out” 6 years before its millennium, disintegrating as a result of a coup d'état.
1100 years (697 AD - 1797 AD)

The Most Serene Republic of Venice with its capital Venice was founded in 697 due to the forced unification of communities against the troops of the Lombards - Germanic tribes who settled in the upper reaches of Italy during the Great Migration of Nations. The extremely favorable geographical position at the crossroads of most trade routes immediately made the Republic one of the richest and most influential states in Europe. However, the discovery of America and the sea route to India was the beginning of the end for this state. The volume of goods entering Europe through Venice decreased - merchants began to prefer more convenient and safe sea routes. The Republic of Venice finally ceased to exist in 1797, when the troops of Napoleon Bonaparte occupied Venice without resistance.
papal states
1118 years (752 AD - 1870 AD)
 Papal States | Wikipedia
Papal States | Wikipedia After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, the influence of Christianity in Europe increased more and more: influential people adopted Christianity, whole lands were given to churches, donations were made. The day was not far off when the Catholic Church would have gained political power in Europe: this happened in 752, when the Frankish king Pepin the Short gave the pope a large area in the center of the Apennine Peninsula. Since then, the power of the popes has fluctuated depending on the place of religion in European society: from absolute power in the Middle Ages, to a gradual loss of influence closer to the 18th and 19th centuries. In 1870, the lands of the Papal States came under the control of Italy, and only the Vatican, a city-state in Rome, remained for the Catholic Church.
Kingdom of Kush
about 1200 years (9th century BC - 350 AD)
The Kingdom of Kush has always been in the shadow of another state - Egypt, which at all times has attracted the attention of historians and chroniclers. Located in the northern part of modern Sudan, the state of Kush posed a serious danger to its neighbors, and during its heyday controlled almost the entire territory of Egypt. We do not know the detailed history of the kingdom of Kush, but the chronicles note that in 350 Kush was conquered by the Aksumite kingdom.
The Roman Empire
1480 years (27 BC - 1453 AD)
Rome is an eternal place on seven hills! At least, that's what the inhabitants of the Western Roman Empire thought: it seemed that the eternal city would never fall before the onslaught of enemies. But times have changed: after the civil war and the founding of the empire, 500 years have passed, and Rome was conquered by the invading Germanic tribes, marking the fall of the western part of the empire. However, the Eastern Roman Empire, often referred to as Byzantium, continued to exist until 1453, when Constantinople fell under the pressure of the Turks.
If you find an error, please highlight a piece of text and click Ctrl+Enter.
The history of mankind is a continuous struggle for territorial domination. Great empires either appeared on the political map of the world or disappeared from it. Some of them were destined to leave an indelible mark.
Persian Empire (Achaemenid Empire, 550 - 330 BC)
Cyrus II is considered to be the founder of the Persian Empire. He began his conquests in 550 BC. e. from the subjugation of Media, after which Armenia, Parthia, Cappadocia and the Lydian kingdom were conquered. Did not become an obstacle to the expansion of the empire of Cyrus and Babylon, whose powerful walls fell in 539 BC. e.
Conquering neighboring territories, the Persians tried not to destroy the conquered cities, but, if possible, to preserve them. Cyrus restored the captured Jerusalem, as well as many Phoenician cities, by facilitating the return of the Jews from the Babylonian captivity.
The Persian Empire under Cyrus stretched its possessions from Central Asia to the Aegean Sea. Only Egypt remained unconquered. The country of the pharaohs submitted to the heir of Cyrus Cambyses II. However, the empire reached its heyday under Darius I, who switched from conquests to domestic politics. In particular, the king divided the empire into 20 satrapies, which completely coincided with the territories of the occupied states.
In 330 B.C. e. the weakening Persian Empire fell under the onslaught of the troops of Alexander the Great.
Roman Empire (27 BC - 476)

Ancient Rome was the first state in which the ruler received the title of emperor. Starting with Octavian Augustus, the 500-year history of the Roman Empire had the most direct impact on European civilization, and also left a cultural mark in the countries of North Africa and the Middle East.
The uniqueness of Ancient Rome is that it was the only state whose possessions included the entire Mediterranean coast.
During the heyday of the Roman Empire, its territories stretched from the British Isles to the Persian Gulf. According to historians, by the year 117 the population of the empire reached 88 million people, which was approximately 25% of the total number of inhabitants of the planet.
Architecture, construction, art, law, economics, military affairs, the principles of the state structure of Ancient Rome - this is what the foundation of the entire European civilization is based on. It was in Imperial Rome that Christianity assumed the status of the state religion and began to spread throughout the world.
Byzantine Empire (395 - 1453)

The Byzantine Empire has no equal in the length of its history. Originating at the end of antiquity, it existed until the end of the European Middle Ages. For more than a thousand years, Byzantium has been a kind of link between the civilizations of the East and the West, influencing both the states of Europe and Asia Minor.
But if the Western European and Middle Eastern countries inherited the richest material culture of Byzantium, then the Old Russian state turned out to be the successor to its spirituality. Constantinople fell, but the Orthodox world found its new capital in Moscow.
Located at the crossroads of trade routes, rich Byzantium was a coveted land for neighboring states. Having reached its maximum borders in the first centuries after the collapse of the Roman Empire, then it was forced to defend its possessions. In 1453, Byzantium could not resist a more powerful enemy - the Ottoman Empire. With the capture of Constantinople, the road to Europe was opened for the Turks.
Arab Caliphate (632-1258)

As a result of the Muslim conquests in the 7th-9th centuries, the theocratic Islamic state of the Arab Caliphate arose on the territory of the entire Middle East region, as well as certain regions of the Transcaucasus, Central Asia, North Africa and Spain. The period of the Caliphate went down in history under the name "Golden Age of Islam", as the time of the highest flowering of Islamic science and culture.
One of the caliphs of the Arab state, Umar I, purposefully secured the character of a militant church for the Caliphate, encouraging religious zeal in his subordinates and forbidding them to own land property in the conquered countries. Umar motivated this by the fact that "the interests of the landowner attract him more to peaceful activities than to war."
In 1036, the invasion of the Seljuk Turks turned out to be disastrous for the Caliphate, but the Mongols completed the defeat of the Islamic state.
Caliph An-Nasir, wishing to expand his possessions, turned to Genghis Khan for help, and without knowing it opened the way for the ruin of the Muslim East to the many thousands of Mongol hordes.
Mongol Empire (1206-1368)

The Mongol Empire is the largest state formation in history in terms of territory.
In the period of its power - by the end of the XIII century, the empire extended from the Sea of Japan to the banks of the Danube. The total area of possessions of the Mongols reached 38 million square meters. km.
Given the vast size of the empire, managing it from the capital - Karakorum was almost impossible. It is no coincidence that after the death of Genghis Khan in 1227, the process of gradual division of the conquered territories into separate uluses began, the most significant of which was the Golden Horde.
The economic policy of the Mongols in the occupied lands was primitive: its essence was reduced to the taxation of tribute to the conquered peoples. All collected went to support the needs of a huge army, according to some sources, reaching half a million people. The Mongol cavalry was the most deadly weapon of the Genghisides, which few armies managed to resist.
The inter-dynastic strife ruined the empire - it was they who stopped the expansion of the Mongols to the West. This was soon followed by the loss of the conquered territories and the capture of the Karakorum by the troops of the Ming Dynasty.
Holy Roman Empire (962-1806)

The Holy Roman Empire is an interstate entity that existed in Europe from 962 to 1806. The core of the empire was Germany, which was joined by the Czech Republic, Italy, the Netherlands, and some regions of France during the period of the highest prosperity of the state.
For almost the entire period of the empire's existence, its structure had the character of a theocratic feudal state, in which emperors claimed supreme power in the Christian world. However, the struggle with the papacy and the desire to possess Italy significantly weakened the central power of the empire.
In the 17th century, Austria and Prussia advanced to leading positions in the Holy Roman Empire. But very soon, the antagonism of two influential members of the empire, which resulted in an aggressive policy, threatened the integrity of their common home. The end of the empire in 1806 was put by the growing France, led by Napoleon.
Ottoman Empire (1299-1922)

In 1299, Osman I created a Turkic state in the Middle East, which was destined to exist for more than 600 years and radically influence the fate of the countries of the Mediterranean and Black Sea regions. The fall of Constantinople in 1453 was the date when the Ottoman Empire finally gained a foothold in Europe.
The period of the highest power of the Ottoman Empire falls on the 16th-17th centuries, but the state achieved the greatest conquests under Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent.
The borders of the empire of Suleiman I stretched from Eritrea in the south to the Commonwealth in the north, from Algiers in the west to the Caspian Sea in the east.
The period from the end of the 16th century to the beginning of the 20th century was marked by bloody military conflicts between the Ottoman Empire and Russia. Territorial disputes between the two states mainly unfolded around the Crimea and Transcaucasia. The First World War put an end to them, as a result of which the Ottoman Empire, divided between the countries of the Entente, ceased to exist.
British Empire (1497¬-1949)

The British Empire is the largest colonial power both in terms of territory and population.
The empire reached its greatest extent by the 30s of the 20th century: the land area of the United Kingdom, together with the colonies, totaled 34 million 650 thousand square meters. km., which was approximately 22% of the earth's land. The total population of the empire reached 480 million people - every fourth inhabitant of the Earth was a subject of the British crown.
Many factors contributed to the success of British colonial policy: a strong army and navy, developed industry, and the art of diplomacy. The expansion of the empire had a significant impact on world geopolitics. First of all, this is the spread of British technology, trade, language, and forms of government around the world.
The decolonization of Britain took place after the end of World War II. The country, although it was among the victorious states, was on the verge of bankruptcy. Only thanks to an American loan of 3.5 billion dollars, Great Britain was able to overcome the crisis, but at the same time it lost world domination and all its colonies.
In terms of area, the Russian Empire was second only to the Mongol and British empires - 21,799,825 sq. km, and was the second (after the British) in terms of population - about 178 million people.
The constant expansion of the territory is a characteristic feature of the Russian Empire. But if the advance to the east was mostly peaceful, then in the west and south Russia had to prove its territorial claims through numerous wars - with Sweden, the Commonwealth, the Ottoman Empire, Persia, the British Empire.
The growth of the Russian Empire has always been viewed with particular caution by the West. The appearance of the so-called "Testament of Peter the Great" - a document fabricated in 1812 by French political circles - contributed to the negative perception of Russia. “The Russian State must establish power over all of Europe,” is one of the key phrases of the Testament, which will haunt the minds of Europeans for a long time to come.
Seizing power must be the dream of at least half of aspiring supervillains. However, some more benevolent (doubtful) people try to do it the old-fashioned way: exploration, colonization, conquest, and sometimes (okay, sometimes) even win-win politics.
Although no one has yet been able to openly seize power (shadow communities do not count), the age of empires was certainly not boring, and as recently as the late 1900s, impressive progress was made.
Let's start all the way from 500 BC and go through it in chronological order to the present. Before you - 25 of the greatest and most powerful empires in the history of mankind!
25. Power of the Achaemenids - about 500 BC
As the 18th largest empire in history, the Achaemenid Empire (also called the first Persian Empire) is already impressive. At its peak around 550 B.C. they occupied an area of 31.6 million km², including the vast majority of the countries of the Middle East and regions of Russia.
Even more impressive, under Cyrus II the Great, the empire had a comprehensive social infrastructure, including roads and a postal service, that other empires would later strive to surpass.
24. Macedonian Empire - circa 323 BC
Under Alexander the Great, the Macedonian Empire destroyed the Achaemenid Empire and built the final Hellenistic state, laying the foundation for ancient Greek civilization, the philosophical contribution of Aristotle, and probably orgies.
At its peak, the Macedonian Empire occupied almost 3.5% of the entire world, making it the 21st largest empire in history (and the second largest after the Persian conquest).
23. Mauryan Empire - circa 250 BC
After the death of Alexander the Great, all of India and most of the surrounding area was conquered by the Mauryan Empire, resulting in the first (and largest) Indian Empire.
At its height, under the benevolent and diplomatic ruler known as Ashok the Great, the Mauryan Empire covered nearly 5 million km², making it the 23rd largest empire in history.
22. Xiongnu Empire - circa 209 BC
During the IV-III centuries. BC, what eventually became China consisted of several warring states. As a result, the Xiongnu's nomadic armies raided the northern territories.
During its heyday, the Xiongnu empire occupied more than 6% of the territory of the whole world, becoming the 10th largest empire in the history of mankind.
They were so irresistible that it took years of negotiations, arranged marriages, and concessions from the Han Dynasty to keep them from conquering.
21. Western Han Dynasty - circa 50 BC
Speaking of the Han dynasties, the Western Han dynasty reached its peak about a century later. Although they never reached the level of development of the Xiongnu empire, they still managed to occupy an area of 6 million km² with over 57 million people, becoming the 17th largest empire in human history. To achieve this, they successfully pushed the Xiongnu north, aggressively expanding south into what is now Vietnam and the Korean peninsula.
The Western Han Dynasty included the major diplomatic achievements of Zhang Qian, who established contacts with states as far west as the Roman Empire and founded the famous trade Silk Road.
20. Eastern Han Dynasty - around 100 AD
During its almost 200 years of existence, the Eastern Han Dynasty has experienced a change of rulers, rebellions, instability and economic crisis. Despite these factors, the Eastern Han dynasty was the 12th largest empire in history. It was larger in area than its pre-Christian counterpart, covering an area of almost 500 km² more - a total of 4.36% of the world.
19. Roman Empire - circa 117 AD
Due to the sheer number of references to the Roman Empire, any average person mistakenly considers it the largest in history.
Indeed, at the height of its heyday in 117 AD. it was the most extensive and social structure in Western civilization, but even then the Romans only occupied a total of 5 million km² of land, making them the 24th largest empire in history.
In this case, the question is not quantity, but quality, since the influence of the Roman Empire affected almost every aspect of Western civilization.
18. Turkic Khaganate - around 557 AD
The Turkic Khaganate consisted of what is currently north-central China. The rulers of the khaganate descended from the Ashina clan, another nomadic tribe of unclear origin from the northern part of Inner Asia.
Like the Xiongnu nearly six centuries earlier, they expanded to rule vast territories in Central Asia, including the lucrative Silk Road trade.
By 557 AD they became the 15th largest empire in history, controlling 4.03% of the entire world (much more than the Roman Empire, which occupied 3.36%).
17. Righteous Caliphate - around 655 AD
The Righteous Caliphate was the first Islamic Caliphate in the earliest period of Islam. It was founded immediately after the death of the Prophet Muhammad in 632 AD to manage the affairs of the Islamic community.
Having subjugated or united with various Arab tribes, the caliphate proceeded to conquer, which led to the dominance of Egypt, Syria and the entire Persian Empire. In his best period in 655 AD. The Righteous Caliphate was the 14th largest empire, covering 6.4 million km² of the Middle East.
16. Umayyad Caliphate - around 720 AD
The second of the four major caliphates after Muhammad's death, the Umayyad Caliphate emerged after the first Muslim civil war in 661 CE. In addition to dominating the entire Middle East, the Umayyad Caliphate continued to expand into North Africa and parts of Southern Europe.
With a complex social structure consisting of 29% of the world's population (62 million people) and 7.45% of the world's land area, the Umayyad Caliphate became the 8th largest empire in modern history and the largest empire in the world that only existed until 720 AD
15. Abbasid Caliphate - around 750 AD
30 years after the heyday of the Umayyad Caliphate, as a result of the rebellion and insubordination of the descendants of the youngest uncle Muhammad to the Umayyads, the Abassid Caliphate came to power.
They claimed that their lineage was closer to the Prophet Muhammad, so they were his true heirs. After the successful seizure of power in 750 AD. they began a "golden age" that lasted almost 400 years and included a strong alliance with China.
Although their empire was no larger than the Umayyad Caliphate, it existed for a long period, successfully controlling 11.1 million km², making them the 7th largest empire in human history until its takeover by Genghis Khan in 1206.
14. Tibetan Empire - around 800 AD
The Tibetan empire occupied more than 3% of the territory of the whole world by 800. At the same time, a comparatively gigantic and prosperous Arab empire flourished from the West. On the other hand, the Tang Dynasty, having become a stable and united force that established diplomatic relations with the Arabs, made the Tibetan Empire one of the first in history to be between two strong states.
Thanks to diplomacy and impressive military power, the Tibetan Empire lasted more than 200 years. Ironically, the growing influence of Buddhist teachings eventually provoked a civil war that split the empire.
13. Tang Dynasty - around 820 AD
The Tang Dynasty ushered in what is considered the golden period of multiculturalism in Chinese civilization. Two of China's most famous poets, Li Bai and Du Fu, belonged to this period, and the invention of woodcuts contributed to the development of artistic culture among the growing population of China and throughout Asia.
Less significant than other Chinese dynasties historically, the Tang Dynasty lasted nearly three centuries (AD 618 to 907), occupying 3.6% of the world's total area and ranking as the 20th largest empire in the world. the history of mankind.
12. Mongol Empire - circa 1270
Although many people know about it, few people really understand how huge the empire of Genghis Khan really was. At its best, the Mongol Empire controlled a whopping 24 million km² of territory.
In comparison, this is more than 4 times the size of the Roman Empire and slightly less than 3 times the size of the modern United States, making the Mongol Empire the 2nd largest empire in human history.
11. Golden Horde - around 1310
Genghis Khan was not stupid, and he knew that without his leadership, the empire would hardly be able to maintain its size. Thus, he divided the empire into regions, and gave control of each to each of his sons in order to preserve his legacy.
Due to the sheer size and power of the original empire, even its individual domains were impressively powerful. In the next generation, after the Mongol Empire reached its peak, it became an independent entity.
Even on its own, by 1310 it was the 16th largest empire in history and controlled a still impressive 4.03% of the world (about a quarter of the land of the Mongol Empire).
10. Yuan Dynasty - circa 1310
From northern Chinese territories already previously controlled by the Mongol Empire, Genghis Khan's grandson led his troops to conquer the rest of China and establish the Yuan Dynasty.
By 1310, it had become the largest fragment of the previous Mongol Empire and the 9th largest empire in human history, with 11 million km² of land in its possession. Unfortunately, rebellions in the mid-14th century led to the eventual overthrow of the Yuan in 1368, making the dynasty the shortest-lived in Chinese history.
9. Ming Dynasty (Great Ming Empire) - around 1450
The Ming Dynasty was formed after the fall of the Yuan Dynasty. Unable to expand north due to the presence of powerful Mongols, the Ming Dynasty still occupied a respectable 4.36% of the world's land area and is the 13th largest empire in history.
She is perhaps best known for building China's first navy, which allowed for maritime expeditions and spurred successful regional maritime trade.
8. Ottoman Empire - circa 1683
When Istanbul was Constantinople, it was the capital of the Ottoman Empire (also called the Turkish Empire). Although historically quite small (5.2 million km², making it the 22nd largest empire in existence), it is otherwise successful and long-lived.
Beginning just before 1300, the Ottoman Empire was able to secure its place between the eastern and western worlds for more than six centuries. After the defeat in the First World War, the empire was destroyed, resulting in the emergence of the Turkish Republic in 1922.
7. Qing Dynasty - circa 1790
The Qing Dynasty was the last imperial dynasty in China. This huge empire became the 4th largest empire in the history of mankind and occupied almost 10% of the entire globe, including the territory of Korea and Taiwan, with a population of over 400 million people.
Nearly three centuries passed before local uprisings forced the last emperor to abdicate, and the Republic of China was established in 1912.
6. Spanish Empire - circa 1810
Not wanting to be left behind by the last Chinese dynasty, the Spanish Empire was formed in 1492 and became only the second global empire in world history. With an area of 15.3 million km² of land under its control, it was the 5th largest in history.
Thanks to numerous naval conquests, they controlled a huge percentage of the territories in both North and South America, as well as virtually all the countries of the Caribbean, parts of Africa, Europe, the South Pacific, and even some cities along the coast of the Middle East.
5. Portuguese Colonial Empire - circa 1820
Also known as the Portuguese Overseas Territories, the Portuguese Colonial Empire became the first global empire in history.
However, it never achieved the same massive dominance as the Spanish Empire. With 3.69% of the Earth under its control, it is the 19th largest empire in history.
Nevertheless, it is the longest-lived modern European colonial empire, having existed for six centuries and almost reaching the new millennium (December 20, 1999, the Portuguese Empire officially ceased to exist).
4. Brazilian Empire - circa 1889
Originally part of the Portuguese Empire, the Brazilian Empire declared its independence in 1822. After several years of instability, a period of calm formed in 1843, which allowed the Brazilian Empire to gain stability until conflicts with Great Britain and Uruguay arose.
After successfully resolving these conflicts, the Brazilian Empire began its "golden age" and quickly became known throughout the world as a progressive and modern nation.
By the 1880s, the empire represented most of South America, covering an area of 8.5 million km², making it the 11th largest empire in human history.
3. Russian Empire - circa 1895
The Russian Empire was a powerful state that existed (officially) from 1721 until it was overthrown in 1917 by a revolution. The empire expanded from the beginning, transforming Russia from a primarily agricultural state into a more modern one.
During its heyday in 1895, the population of the Russian Empire grew from 15.5 million to 170 million people, living on an area of almost 23.3 million km². With the addition of the Baltic States, Poland, Finland and more significant Asian territories to its territory, the Russian Empire became the 3rd largest in the history of mankind.
2. Second French colonial empire - circa 1920
Competing with Spain, Portugal, the United Provinces and (later) Britain, the Second French Colonial Empire began in 1830 with the conquest of Algiers. They colonized a large percentage of Africa and took possession of the Middle East, Southeast Asia, New Caledonia and a tiny part of South America.
This made the empire in its heyday the 6th largest in history, as its population was 5% of the total population of the globe, and they lived on 7.7% of the Earth.
1. British Empire - circa 1920
It may or may not shock you, but in the competition to conquer the world, there has never been a more dominant empire than the British. Covering an area of 35.5 million km², the British Empire easily became the largest in the history of mankind (30% larger than the Mongol Empire).
For more than a century, Britain was the world's main superpower and controlled 23% of the world's population. As a result of massive expansion around the world, their cultural and linguistic heritage can be found in almost every advanced culture on Earth.
Most consider the official handover of Hong Kong to China in 1997 as the official end of the British Empire. Although if you look at the world stage, the UK still controls the largest part of the world ... they just do it very smartly and more progressively. Perhaps this is world domination ... just cleverly implemented.









