On January 12, 2005, a powerful earthquake occurred on the island of Haiti; the magnitude of the tremors reached 7. More than 222 thousand people became victims of the disaster. On the fifth anniversary of the tragedy, we decided to recall the most destructive earthquakes of the 21st century
Afghanistan. 2002
In March 2002, two powerful earthquakes rocked northern Afghanistan. The magnitude of the tremors exceeded 7. About two thousand people became victims of the disaster, and about 20 thousand more Afghans were left homeless.
The first earthquake in northern Afghanistan after four years of calm was recorded on March 3, 2002 at about 15:00 Moscow time. The magnitude of the tremors was 7.2. Soil vibrations were felt over a wide area - from Tajikistan to India. The epicenter was on the Afghanistan-Pakistan border in the Hindu Kush mountains. More than 100 people died then, and dozens more went missing. Representatives of the World Food Program, who were in Kabul at that time, provided assistance to the victims. Helicopters, which were previously used to deliver humanitarian aid, were sent to two of the most affected villages in the north of Samangan province.
22 days later, on March 25, 2002, disaster struck Afghanistan again. Underground points with magnitudes from 6.5 to 7 were recorded in the northeast of the country. The epicenter of the earthquake was 50 kilometers southeast of the city of Kunduz. This time the disaster claimed the lives of about one and a half thousand people, more than four thousand people were injured, and about one and a half thousand buildings were completely destroyed. Baghlan province was the hardest hit. The city of Nahrin was completely destroyed. The forces of the Russian Ministry of Emergency Situations were involved in the rescue operation. For several more days, tremors were felt in Kabul, Mazar-i-Sharif, as well as in the Pakistani city of Peshawar and Tajikistan.
Iran. 2003
On December 26, 2003 at 5:26 local time, a deep, destructive earthquake shook the southeast of Iran. The disaster completely destroyed the ancient city of Bam. Several tens of thousands of people became victims of the earthquake.
The epicenter of the tremors, with a magnitude of 6.7 to 5, was recorded in the southeast of Iran, several tens of kilometers from the large city of Bam. The country's authorities urgently turned to the international community asking for help. More than 60 countries responded to the call, with 44 sending personnel to help deal with the disaster. Russia also took part in the rescue operation.
Already in the first hours after the earthquake, it was clear that the disaster spared few people - the number of victims was in the tens of thousands. According to official figures, 35 thousand people died, but later the Iranian Minister of Health reported 70 thousand victims. In addition, Bam was practically wiped off the face of the earth - up to 90% of the buildings were destroyed, many of which were made of clay. As a result, the Iranian government decided not to restore the ancient city, but to build a new one in its place.
Indonesia. 2004
On December 26, 2004 at 07:58 local time, one of the most destructive earthquakes in modern history occurred in the Indian Ocean. The magnitude of the tremors reached 9.3. Following this, Indonesia, Sri Lanka, southern India, Thailand and 14 other countries were hit by a tsunami. The wave destroyed everything in its path. Up to 300 thousand people became victims of the disaster.

Exactly a year later, to within an hour after the earthquake in Iranian Bam, underground points were felt by residents of Indonesia. The epicenter of the earthquake this time was in the Indian Ocean, north of the Indonesian island of Simeulue, located off the northwestern coast of the Indonesian island of Sumatra. The earthquake, which became the third strongest earthquake on record, triggered waves up to 30 meters high. Within 15 minutes they reached the shores of the nearest countries; the tsunami reached the most remote corners of the Indian Ocean seven hours later. Many states were not prepared for such a disaster - most coastal zones were taken by surprise. People went to the coast to collect fish that suddenly appeared on land, or to admire an unusual natural phenomenon - this was the last thing they saw.
The disaster killed hundreds of thousands of people. The exact number of deaths has not yet been established - it ranges from 235 thousand people to 300 thousand, tens of thousands are missing, more than a million people were left without homes. Thousands of tourists from different parts of the world who decided to celebrate the Christmas and New Year holidays in the Indian Ocean never returned home.
Pakistan. 2005 year
On October 8, 2005 at 8:50 local time, a powerful earthquake was recorded in Pakistan. The magnitude of the tremors was 7.6. According to official data, more than 74 thousand people were killed, including 17 thousand children, and about three million more Pakistanis were left homeless.

The epicenter of the earthquake was located in the Pakistani region of Kashmir, 95 kilometers from Islamabad. The source of the tremors lay at a depth of 10 kilometers. The earthquake was felt by residents of several countries. The disaster caused major destruction in northeastern Pakistan, Afghanistan and northern India. Many villages were destroyed to the ground. To date, the earthquake in Kashmir is the worst in South Asia in the last 100 years.
Several states offered assistance in eliminating the consequences of the rampant disaster to Pakistan. International and non-governmental organizations provided assistance in the form of money, food and medical equipment. Cuba provided special support to Pakistan, sending about a thousand doctors to the disaster zone in the first days after the tragedy.
The exact number of earthquake victims is still unknown. According to the authorities, 84 thousand people died in October 2005, but according to unconfirmed information, the disaster claimed the lives of up to 200 thousand people.
China. 2008
On May 12, 2008, at 14:28 Beijing time, an earthquake of magnitude 8 occurred in the Chinese province of Sichuan. The disaster claimed the lives of about 70 thousand people, and another 18 thousand were missing.
The epicenter of the earthquake was recorded 75 kilometers from the capital of Sichuan province, Chengdu; the source of the tremors lay at a depth of 19 kilometers. The main earthquake was followed by over ten thousand aftershocks. The echoes of the earthquake reached Beijing, which was located one and a half thousand kilometers from the epicenter. Tremors were also felt by residents of India, Pakistan, Thailand, Vietnam, Bangladesh, Nepal, Mongolia and Russia.
According to official data, more than 69 thousand people became victims of the rampant disaster, 18 thousand are listed as missing, 370 thousand were injured, and five million Chinese were left homeless. The Sichuan earthquake became the second most powerful in the modern history of China, in first place is the Tangshan earthquake, which occurred in 1976 and claimed about 250 thousand lives.
Haiti. 2010
On January 12, 2010 at 16:53 local time, the island nation of Haiti was rocked by a powerful earthquake. The magnitude of the tremors reached 7. The disaster completely destroyed the capital of Port-au-Prince. The death toll exceeded 200 thousand people.
 After the first earthquake in Haiti, many aftershocks were recorded, 15 of them with a magnitude greater than 5. The epicenter of the earthquake was 22 kilometers southwest of the capital of the island state, the source lay at a depth of 13 kilometers. Geological services later explained that the Haiti earthquake was the result of the movement of the earth's crust in the contact zone of the Caribbean and North American lithospheric plates.
After the first earthquake in Haiti, many aftershocks were recorded, 15 of them with a magnitude greater than 5. The epicenter of the earthquake was 22 kilometers southwest of the capital of the island state, the source lay at a depth of 13 kilometers. Geological services later explained that the Haiti earthquake was the result of the movement of the earth's crust in the contact zone of the Caribbean and North American lithospheric plates.
The authorities of 37 countries, including Russia, sent rescuers, doctors and humanitarian aid to Haiti. However, the international rescue operation was hampered by the fact that the airport could not cope with the large number of arriving aircraft, and there was not enough fuel to refuel them. Media reported that earthquake survivors were dying in droves from severe shortages of clean water, food, medicine and medical care.
According to official data, the disaster claimed the lives of more than 222 thousand people, another 311 thousand were injured, and more than 800 people are listed as missing. In Port-au-Prince, the disaster destroyed several thousand residential buildings and almost all hospitals, leaving about three million people homeless.
Japan. 2011
On March 11, 2011 at 14:46 local time, a powerful earthquake occurred off the east coast of Honshu Island in Japan. The magnitude of the tremors reached 9.1. The disaster claimed the lives of 15,870 people, and another 2,846 are listed as missing.

The epicenter of the tremors was located 373 kilometers northeast of Tokyo, the source lay in the Pacific Ocean at a depth of 32 kilometers. The main shock of magnitude 9.0 was followed by a series of aftershocks, more than 400 of them in total. The earthquake caused a tsunami that spread throughout the Pacific Ocean, the wave reaching Russia.
According to official data, the death toll as a result of the earthquake and tsunami in 12 prefectures of Japan is 15,870 people, another 2,846 people are missing, and more than six thousand people were injured. The rampant nature led to an accident at the Fukushima-1 nuclear power plant. The earthquake and tsunami disabled external power supplies and backup diesel generators, which led to the breakdown of all normal and emergency cooling systems, which in turn caused meltdowns of the reactor cores at three power units.
Fukushima 1 was officially closed in December 2013. Work to eliminate the consequences of the accident continues to this day on the territory of the nuclear power plant. Experts estimate that bringing the facility into a stable state may take up to 40 years.
Major earthquakes have occurred throughout human history, with the earliest recorded dating back almost 2,000 BC. But it is only in the last century that our technological capabilities have reached the point where the impact of these disasters can be fully measured. Our ability to study earthquakes has made it possible to avoid catastrophic casualties, such as in the case of a tsunami, when people have the opportunity to evacuate a potentially dangerous area. But unfortunately, the warning system does not always work. There are several examples of earthquakes where the greatest damage was caused by the subsequent tsunami, and not by the earthquake itself. People have improved building standards and improved early warning systems, but they have never been able to completely protect themselves from disasters. There are many different ways to estimate the strength of an earthquake. Some people rely on the Richter scale, others on the number of deaths and injuries, or even the monetary value of the damaged property. This list of the 12 strongest earthquakes combines all of these methods in one.
Lisbon earthquake
The Great Lisbon Earthquake struck the Portuguese capital on November 1, 1755, causing enormous destruction. They were made worse by the fact that it was All Saints' Day and thousands of people attended mass in the church. Churches, like most other buildings, could not withstand the elements and collapsed, killing people. Subsequently, a tsunami 6 meters high hit. An estimated 80,000 died due to fires caused by the destruction. Many famous writers and philosophers dealt with the Lisbon earthquake in their works. For example, Emmanuel Kant, who tried to find a scientific explanation for what happened.
California earthquake
A major earthquake struck California in April 1906. Etched into history as the San Francisco earthquake, it caused damage to a much wider area. Downtown San Francisco was destroyed by a huge fire that followed. Initial figures mentioned 700 to 800 dead, although researchers claim the actual death toll was more than 3,000. More than half of San Francisco's population lost their homes as 28,000 buildings were destroyed by the earthquake and fires.

Messina earthquake
One of Europe's largest earthquakes struck Sicily and southern Italy in the early hours of December 28th, 1908, killing an estimated 120,000 people. The main epicenter of the damage was Messina, which was virtually destroyed by the disaster. The magnitude 7.5 earthquake was accompanied by a tsunami that hit the coast. A recent study suggested that the size of the waves was so huge because of an underwater landslide. Much of the damage was due to the poor quality of buildings in Messina and other parts of Sicily. 
Haiyuan earthquake
One of the deadliest earthquakes on the list occurred in December 1920, with its epicenter in Haiyuan Chingya. At least 230,000 people died. Measuring 7.8 on the Richter scale, the earthquake destroyed almost every home in the region, causing significant damage to major cities like Lanzhou, Taiyuan and Xi'an. Incredibly, waves from the earthquake were visible even off the coast of Norway. According to a recent study, Haiyuan was the strongest earthquake to hit China during the 20th century. Researchers have also questioned the official death toll, suggesting there may have been more than 270,000. This number represents 59 percent of the population in the Haiyuan area. The Haiyuan earthquake is considered one of the most destructive natural disasters in history.
Chilean earthquake
A total of 1,655 were killed and 3,000 were injured after a magnitude 9.5 earthquake struck Chile in 1960. Seismologists called it the strongest earthquake ever to occur. 2 million people were left homeless and economic losses amounted to $500 million. The force of the earthquake caused a tsunami, with casualties in places as far away as Japan, Hawaii and the Philippines. In some parts of Chile, waves have moved building ruins 3 kilometers inland. The massive Chilean earthquake of 1960 caused a giant rupture in the ground extending over 1,000 kilometers. 
Earthquake in Alaska
On March 27th, 1964, a strong 9.2 earthquake struck the Prince William Sound region of Alaska. As the second most powerful earthquake on record, it caused a relatively low number of deaths (192 deaths). However, significant property damage occurred in Anchorage, and tremors were felt in all 47 US states. Due to significant improvements in research technology, the Alaska earthquake has provided scientists with valuable seismic data, allowing them to better understand the nature of such events. 
Kobe earthquake
In 1995, Japan was hit by one of its most powerful earthquakes when a magnitude 7.2 shock struck the Kobe region in south-central Japan. Although it was not the worst ever seen, the devastating impact was felt by a significant portion of the population—an estimated 10 million people living in the densely populated area. A total of 5,000 were killed and 26,000 were injured. The US Geological Survey estimated damage at $200 billion, with infrastructure and buildings destroyed. 
Sumatra and Andaman earthquake
The tsunami that struck across the Indian Ocean on December 26, 2004 killed at least 230,000 people. It was caused by a large undersea earthquake off the west coast of Sumatra, Indonesia. His strength was measured at 9.1 on the Richter scale. The previous earthquake in Sumatra occurred in 2002. It is believed to have been a seismic pre-shock, with several aftershocks occurring throughout 2005. The main reason for the huge number of casualties was the lack of any early warning system in the Indian Ocean capable of detecting an approaching Tsunami. A giant wave reached the shores of some countries, where tens of thousands of people died, for at least several hours. 
Kashmir earthquake
Jointly administered by Pakistan and India, Kashmir was hit by a magnitude 7.6 earthquake in October 2005, killing at least 80,000 people and leaving 4 million homeless. Rescue efforts were hampered by conflicts between the two countries fighting over the territory. The situation was aggravated by the rapid onset of winter and the destruction of many roads in the region. Eyewitnesses spoke of entire areas of cities literally sliding off cliffs due to the destructive elements. 
Disaster in Haiti
Port-au-Prince was hit by an earthquake on January 12, 2010, leaving half the capital's population without their homes. The death toll is still disputed and ranges from 160,000 to 230,000. A recent report highlighted that as of the fifth anniversary of the disaster, 80,000 people continue to live on the streets. The impact of the earthquake has caused severe poverty in Haiti, which is the poorest country in the Western Hemisphere. Many buildings in the capital were not built in accordance with seismic requirements, and the people of the completely destroyed country had no means of subsistence other than the international aid provided. 
Tohoku earthquake in Japan
The worst nuclear disaster since Chernobyl was caused by a magnitude 9 earthquake off the east coast of Japan on March 11, 2011. Scientists estimate that during the 6-minute earthquake of colossal force, 108 kilometers of the seabed rose to a height of 6 to 8 meters. This caused a large tsunami that damaged the coast of Japan's northern islands. The Fukushima nuclear power plant was badly damaged and efforts to salvage the situation are still ongoing. The official death toll is 15,889 dead, although 2,500 people are still missing. Many areas have become uninhabitable due to nuclear radiation. 
Christchurch
The worst natural disaster in New Zealand's history claimed 185 lives on February 22, 2011, when Christchurch was hit by a powerful 6.3 magnitude earthquake. More than half of the deaths were caused by the collapse of the CTV building, which was built in violation of seismic codes. Thousands of other houses were also destroyed, including the city's cathedral. The government declared a state of emergency in the country so that rescue efforts could proceed as quickly as possible. More than 2,000 people were injured, and reconstruction costs exceeded $40 billion. But in December 2013, the Canterbury Chamber of Commerce said that three years after the tragedy, only 10 per cent of the city had been rebuilt.
As earthquake statistics show, seismological disasters account for 13% of the total number of natural ones. Over the past hundred years, about 2,000 tremors with a magnitude of 7 or more have occurred in the world. Of these, 65 cases exceeded the 8 mark.
World situation
If you look at a world map on which seismological activity is displayed as dots, you will notice one pattern. These are some characteristic lines along which tremors are intensely recorded. The tectonic boundaries of the earth's crust are located in these zones. Statistics have established that strong catastrophic earthquakes, which entail the most destructive consequences, occur due to tension in the source of “rubbing in” of tectonic plates. 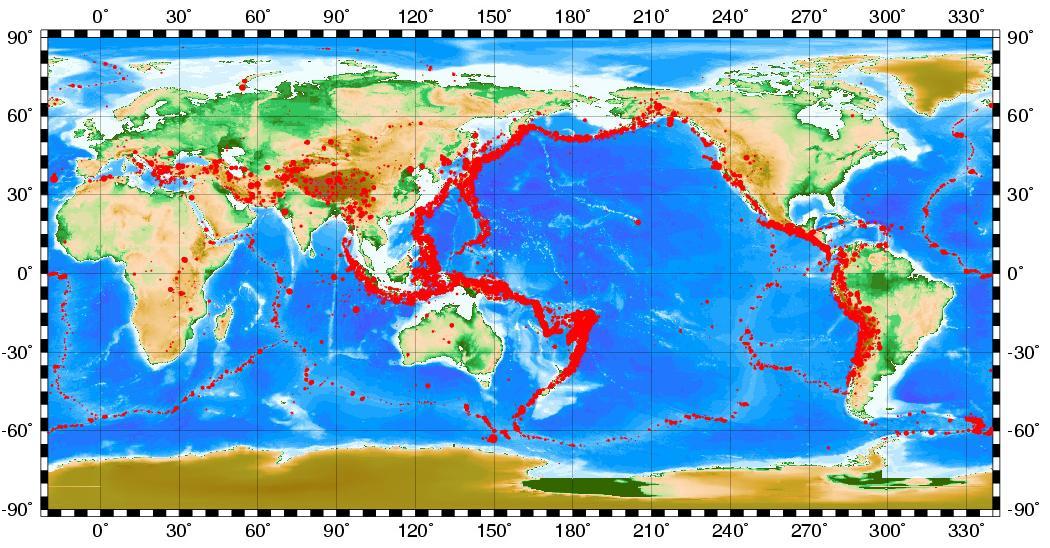
Earthquake statistics over 100 years show that about a hundred seismic disasters occurred on continental tectonic plates (not oceanic) alone, in which 1.4 million people died. A total of 130 strong earthquakes were recorded during this period.
The table shows the largest known seismic disasters since the 16th century:
| Year | Scene of the incident | Destruction and casualties |
| 1556 | China | The victims were 830 thousand people. According to current estimates, the earthquake can be assigned the highest rating - 12 points. |
| 1755 | Lisbon (Portugal) | The city was completely destroyed, 100 thousand inhabitants died |
| 1906 | San Francisco (USA) | Most of the city was destroyed, 1,500 people became victims (7.8 points) |
| 1908 | Messina (Italy) | The destruction claimed 87 thousand lives (magnitude 7.5) |
| 1948 | Ashgabat (Turkmenistan) | 175 thousand people died |
| 1960 | Chile | The largest earthquake recorded in the last century. It was rated 9.5 points. Three cities were destroyed. About 10 thousand residents became victims |
| 1976 | Tien Shan (China) | Magnitude 8.2. 242 thousand people died |
| 1988 | Armenia | Several cities and towns were destroyed. More than 25 thousand victims were recorded (7.3 points) |
| 1990 | Iran | About 50 thousand inhabitants died (magnitude 7.4) |
| 2004 | Indian Ocean | The epicenter of the 9.3 magnitude earthquake was at the bottom of the ocean, which killed 250 thousand people |
| 2011 | Japan | An earthquake with a magnitude of 9.1 caused the death of more than 15 thousand people and had enormous economic and environmental consequences not only for Japan, but for the whole world. |
Over the 30 years of the end of the 20th century, about 1 million people died in seismic disasters. This is approximately 33 thousand per year. Over the past 10 years, earthquake statistics show an increase in the average annual figure to 45 thousand victims.  Every day, hundreds of imperceptible vibrations of the earth's surface occur on the planet. This is not always associated with the movement of the earth's crust. Human actions: construction, mining, blasting - all of them entail vibrations that are recorded by modern seismographs every second. However, since 2009, the USGS geological service, which collects data on earthquake statistics in the world, has stopped taking into account tremors below 4.5 points.
Every day, hundreds of imperceptible vibrations of the earth's surface occur on the planet. This is not always associated with the movement of the earth's crust. Human actions: construction, mining, blasting - all of them entail vibrations that are recorded by modern seismographs every second. However, since 2009, the USGS geological service, which collects data on earthquake statistics in the world, has stopped taking into account tremors below 4.5 points.
Crete
The island is located in a tectonic fault zone, so increased seismological activity there is a frequent occurrence. According to statistics, earthquakes in Crete do not exceed 5 points. With such force, there are no destructive consequences, and local residents do not pay any attention to this shaking. On the graph you can see the number of registered seismic shocks by month with a magnitude greater than 1 point. You can see that their intensity has increased somewhat in recent years. 
Earthquakes in Italy
The country is located in a zone of seismic activity on the territory of the same tectonic fault as Greece. Earthquake statistics in Italy over the past 5 years show an increase in the number of monthly tremors from 700 to 2000. In August 2016, a strong earthquake with a magnitude of 6.2 occurred. That day claimed the lives of 295 people and injured more than 400.
In January 2017, another earthquake with a magnitude of less than 6 occurred in Italy; there were almost no casualties from the destruction. However, the shock was caused in the province of Pescara. The Rigopiano Hotel was buried under it, killing 30 people.
There are resources that display earthquake statistics online. For example, the IRIS organization (USA), which collects, systematizes, studies and distributes seismological data, presents a monitor of this type:  The website contains information showing the presence of earthquakes on the planet at the moment. Here their magnitude is shown, there is information for yesterday, as well as events from 2 weeks or 5 years ago. You can take a closer look at the areas of the planet you are interested in by selecting the appropriate map from the list.
The website contains information showing the presence of earthquakes on the planet at the moment. Here their magnitude is shown, there is information for yesterday, as well as events from 2 weeks or 5 years ago. You can take a closer look at the areas of the planet you are interested in by selecting the appropriate map from the list.
The situation in Russia
According to earthquake statistics in Russia and the OSR (General Seismic Zoning) map, more than 26% of the country's area is located in seismically hazardous zones. Tremors of magnitude 7 may occur here. This includes Kamchatka, the Baikal region, the Kuril Islands, Altai, the North Caucasus and the Sayan Mountains. There are about 3,000 villages, about 100 thermal power plants and hydroelectric power stations, 5 nuclear power plants and enterprises of increased environmental hazard.
Krasnodar region
The zone contains about 28 districts of the region, with a population of approximately 4 million people. Among them is the large resort city of Sochi - according to earthquake statistics, the last seismic activity above 4 points was registered in the fall of 2016. Kuban is mostly located in the zone of magnitude 8–10 earthquakes (MSK-64 scale). This is the highest seismic hazard index throughout the Russian Federation.
The reason is the resumption of tectonic processes in 1980. Earthquake statistics in the Krasnodar region annually record about 250 seismic shocks of more than 2 points. Since 1973, 130 of them have been force 4 or higher. Tremors with a magnitude greater than 6 are recorded once every 5 years, and above 7 - once every 11 years. 
Irkutsk
Due to its location near the Baikal Rift, earthquake statistics for Irkutsk record up to 40 minor tremors every month. In August 2008, seismic activity with a magnitude of 6.2 was recorded. The epicenter was in Lake Baikal, where the indicator reached 7 points. Some buildings were cracked, but no significant damage or casualties were recorded. In February 2016, another earthquake of magnitude 5.5 occurred.
Ekaterinburg
Despite the fact that the growth of the Ural Mountains has long ceased, the statistics of earthquakes in Yekaterinburg continues to be updated with new data. In 2015, an earthquake of magnitude 4.2 was recorded there, but there were no casualties.
Conclusion
Between the end of 2008 and 2011, there was a decrease in seismic activity on the planet, to a level of less than 2,500 events per month and a magnitude above 4.5. However, after the earthquake in Japan in 2011, between 2011 and 2016 there was a tendency for earthquake activity around the world to almost double. The earthquake statistics for recent years are as follows:
- tremors from 8 points and above – 1 time/year;
- from 7 to 7.9 points – 17 times/year;
- from 6 to 6.9 – 134 times/year;
- from 5 to 5.9 – 1319 times/year.
 Predicting earthquakes is very difficult. It is often possible to say with certainty where it will happen, but when exactly it will happen is impossible to determine. However, there are biological precursors. On the eve of a strong earthquake, other representatives of the fauna living in this territory begin to behave abnormally.
Predicting earthquakes is very difficult. It is often possible to say with certainty where it will happen, but when exactly it will happen is impossible to determine. However, there are biological precursors. On the eve of a strong earthquake, other representatives of the fauna living in this territory begin to behave abnormally.
The history of mankind remembers a lot of cataclysms, the most dangerous of which, for good reason, are earthquakes. The power of such natural incidents is assessed on the Richter scale. We propose to recall the top 10 most powerful earthquakes in the history of the Earth. We are talking about the most devastating seismic hazards that have taken the lives of millions of people. At the same time, humanity still remembers the dates of terrible events, which even modern technology and progress could not avoid. So, let's get started with the review:
TOP 10 most destructive earthquakes

It is worth noting that the most powerful earthquakes in the history of the world were recorded in Chile. The last of these occurred in 2010. The power of magnetic influence on the Richter scale is estimated at 8.8 points. The epicenter of the threat was in the city of Bio-Bio Concepción. The residents of this locality and the city of Maule suffered the most. A total of 540 people died in Bio-Bio Concepción. In the territory of the second city, 64 people were injured. Approximately 2 million people were left homeless. In total, damage is estimated at $30 billion.

The tsunami that occurred on January 31 in Ecuador immediately hit the entire coast of Central America. A magnitude of 8.8 was recorded in San Francisco. The first wave even reached Japan. Fortunately, we managed to get by with a minimum number of casualties due to the low population density. According to preliminary estimates, 1,500 people were affected and left without homes. Due to the timely response of rescuers, no fatalities were found. However, the damage is estimated at $1.5 million.

One of the most powerful earthquakes in history is considered to be a seismic shock recorded in 1923 near the island of Oshima. As a result of the incident, nearly three hundred thousand buildings in Tokyo and Yokohama were destroyed. Over two days, 356 tremors occurred. As a result, the waves reached a height of 12 meters. The tsunami took the lives of 174 thousand people. About 542 thousand are considered missing. In total, damage is estimated at $4.5 billion.

As a result of this cataclysm, over 820 thousand people died. The number of victims is considered the most serious incident in history. The disaster went down in history due to its duration. The horror lasted for nearly three days. During this time, the entire component of Shaanxi province was destroyed, including 60% of the population of the locality. The epicenter affected three provinces, including Feinan and Huaxian. A magnetic source was recorded in the Wei Valley. It is difficult to assess the damage due to the time span of the events.

In 2011, a magnitude of 9.1 was recorded on the island of Honshu. The most powerful earthquake in the history of Japan occurred 130 kilometers from the city of Sendai. About 30 minutes later, a powerful tsunami hit the coast of the country, which destroyed 11 nuclear power units in 69 minutes. As a result, 6,000 people died. 2,000 Japanese were missing. In total, the country suffered $36.6 billion in damage. To this day, local residents remember March 11 with horror.

As a result of a powerful earthquake on November 5, 1952, a tsunami reached the city of Severo-Kurilsk. As a result of a seismic phenomenon with a magnitude of 9 points, a powerful tsunami destroyed the entire city. According to rough estimates, the wave took the lives of 2,336 people. At the same time, about 6,000 people are considered missing. The waves reached 18 meters in height. The damage even at that time was $1 million. A total of three waves were observed. The weakest of them reached a height of 15 meters.

On December 26, an underwater earthquake with a scale of 9.3 reached the Indonesian island of Sumatra. The source of the cataclysm was provoked by the most destructive tsunami in human history. Waves of 15 meters destroyed Sri Lanka, southern India and the coast of Indonesia. Even the residents of Thailand suffered damage. The tsunami almost completely destroyed the infrastructure of eastern Sri Lanka. According to preliminary estimates, nearly 225 thousand people died. At the same time, another 300 thousand are considered missing. Preliminary estimates put the damage at $10 billion.

This happened in the northern Gulf of Alaska. Power is 9.2 points. The epicenter of the terrible earthquake was recorded 120 kilometers from the western part of Seward. The tremors led to the destruction of Kodiak Island and the city of Valdese. The shock itself killed 9 people. The tsunami killed 190 people. The mortality rate was reduced thanks to the timely detection of the threat. However, California suffered $200 million in damages. Destruction stretched from Canada to California.









