Menu principles and rules
1. The amount of energy coming from food should approximately correspond to the amount of energy expended.
2. The best ratio of protein, fat and carbohydrates - 1: 1: 4
3. Food should be varied. Daily diet should contain the recommended amount and ratio of proteins, fats and carbohydrates, minerals and vitamins.
In the daily diet of an adult should be
PROTEINS(meat, fish, dairy products, eggs) - 12% of the total calorie intake
80-90 gr. (of which animal proteins 55% or 44-50 gr.).
FATS - 33% of the total calorie intake.
100-105 gr. (of which 30% vegetable fats or about 30 gr.).
CARBOHYDRATES 55% of the total calorie intake.
365-400 gr. (average 382 grams), incl. simple - not > 50-100 gr. and dietary fiber (fiber and pectin) - 10-15 grams.
3 times food: breakfast 30% of the daily calorie intake, lunch 45-50% and dinner 20-25%.
4-5 times food: breakfast - 25% of the daily diet, 2nd breakfast 5%, lunch 45% of the diet; afternoon snack 5% and dinner (20%).
200 gr. meat equivalent to 200 gr. fish or poultry, 6 eggs, 300 gr. cottage cheese, 1.2 liters of milk.
This gives 35-40 gr. animal protein per day: close to the required physiological norm (47 gr.) for an adult engaged in light physical labor. The protein norm during the week can vary within ± 20%.
Vegetarian (fast days) once a week are useful for people over 40 and not engaged in hard physical work. Fish can be included in the menu 2-3 times a week instead of meat, and legumes - 1 time in 2 weeks instead of cereals.
Products that should be on the menu constantly:
Sources of vit. WITH - sauerkraut, lemons, rose hips, etc.
Sources of vit. B1 and RR- wholemeal bread and meat, vit. B2 - milk (0.5 liters - ½ daily requirement).
Average daily bread- 330 gr. (this is ½ daily requirement of vitamins B1 and PP, 10 mg of iron).
calcium and phosphorus- in milk, meat and fish,
Iron- in wholemeal bread and meat.
Vegetable oils- a source of essential polyunsaturated fatty acids (daily norm is about 20-25 grams).
Food losses during cooking (cold and heat).
The actual amount of food consumed is less than that bought in the store by 15-60%, depending on the type of product, and on average - by 1/3.
Cold working- cleaning cereals from impurities (loss 1-2%), removing the crust on cheese (loss 2-4%), cleaning vegetables from the ground, removing damaged parts (loss within 10-30%, including 28% potatoes , 20% white cabbage, 20% carrots and beets, 10% eggplant), cleaning fruits and berries from seeds (12% apples, 10% pears, 13% grapes), cleaning meat from bones and tendons (25-29% beef, 26-32% lamb, 12-15% pork, 28-33% gutted poultry), cleaning fish from fins, head, bones, and skin (average 40-55%, including 54% carp, 42 % chum salmon, 54% pollock, 40% halibut, 49% pike perch, 51% cod, 57% pike).
Losses during heat treatment depend on its type (frying, boiling, baking), are summed up with losses during direct consumption (during portioning, leftovers on the plate, accidental spoilage, etc.) and in total amount to for proteins 10%, for fats - 16%, for carbohydrates - 15%.
With completely homemade food, the entire diet can be divided into three parts: breakfast, lunch (slightly more calories than breakfast) and dinner (slightly fewer calories than breakfast).
An approximate distribution of products for the day may look like this.
For breakfast. A piece of boiled meat or fish (no more than 40-70 grams) with a vegetable or potato garnish or cottage cheese (100 grams) with sour cream, or scrambled eggs from 2 eggs (in the last two cases, salad or vinaigrette is served additionally). Then tea or coffee, or a glass of warm milk. Bread - 120 grams.
At lunch. For a snack salad or vinaigrette seasoned with sunflower oil, you can just chopped cabbage or grated carrots. Liquid first course - soup, borscht, broth. The second dish is preferably meat or fish (50-100 grams) with a vegetable or potato side dish. On the third - a glass of juice, compote or one apple. Bread - 150 grams.
For dinner. Salad, cheesecakes or cottage cheese pudding (50-100 grams). Tea or a glass of milk. Bread - 60 grams.
Before bedtime- a glass of kefir or yogurt.
With reduced body weight the menu should include additional cereals (oatmeal, buckwheat, rice) for breakfast. To garnish meat dishes potatoes, cereals should be served.
With excess body weight meals should be 4-5 times a day, the menu should include vegetables and animal products. Cereals, bread and potatoes, animal fats (lard, butter) must be limited. Fasting days are useful, at least once a week - "dairy", "vegetable", "fruit", when only low-calorie foods are used in the diet.
Protein digestibility
Proteins of meat, milk, fish, eggs are digested by 96-98%, proteins of rye bread of ordinary grinding are not > 70-75%, millet proteins - 60-65%.
Digestibility of mixed food proteins(from products of living and plant origin) - from 80 to 90%. When replacing part of cereals and bread with vegetables, the digestibility increases to 85-90%.
Approximate daily set of products
(for 2800-2950 kcal, B=80-90 g, F=100-105 g, Y=380-385 g)
Bread in terms of flour - 255 g;
pasta - 15 g;
cereals - 25 g;
legumes - 5 g;
potatoes - 265 g;
vegetables and melons - 450 g (including 100 g of cabbage);
fruits, berries (fresh and canned) - 220 g (1/2 - apples);
sugar (directly and included in confectionery, bread and other products) - no more than 50-100 g;
vegetable oil and products from it - 36 g;
meat and products from it - 192 g;
fish and products from it - 50 g;
milk and dairy products in terms of milk - 986 g (including 400-500 g of milk directly);
eggs - at the rate of 2 pcs. at 3 days.
For the convenience of calculating the daily diet, take the average daily set of products.
In order to create a menu for the week from this set of products, the number of all products, with the exception of bread, is multiplied by 7 and distributed according to the days of the week (pasta at an average daily rate is recommended in the amount of 10 g, per week - 70 g: 2 times 35 g as a side dish for meat, or 1 times - just boiled macaroni and cheese, or pasta casserole, etc.).
You need to eat so that when you finish your meal you will be a little hungry! Because the more we eat, the more we want to eat! The stomach is expanding and it needs to receive food no less than yesterday. But this does not mean that the body needs extra food. Very little is needed to sustain life.
It is important to eat little by little. Then the body does not "spoil". And when you go on a strict diet and limit yourself to food for for a long time, this leads to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Because the body is so arranged that when the time comes to eat, and you do not eat, then the natural digestive processes . Gastric juice is produced to digest food, but food is not delivered. Gastric juice begins to corrode the walls of the stomach. The body does not receive energy and as a result uses up its reserves. But the reserves must be replenished with vitamins, minerals, carbohydrates, fats, proteins. When all the reserves of the body are exhausted, then appearance This person leaves a lot to be desired! Of course, this does not apply to overweight people. They just need to spend their "reserves"!
Daily food intake
what should be in calories? For a person working in an office, it is approximately 2000 cal. For athletes, it can reach 5000 cal. calories is the energy necessary for human life. To calculate the daily amount of kcal needed for a person, you need to calculate your norm from the calorie table of products (see table). So 1 g of fat contains 9 calories, and 1 g of carbohydrates or proteins - 4 calories. 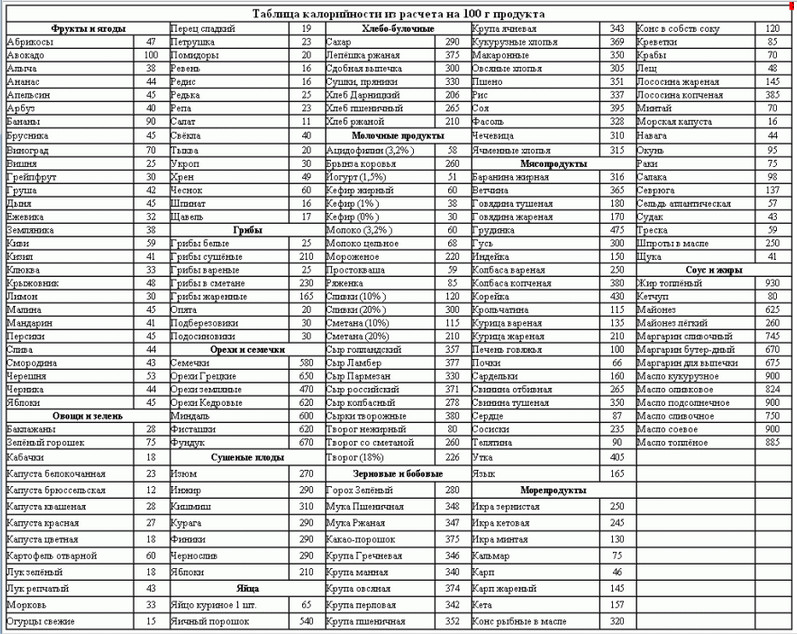
Breakfast- if for breakfast you eat 1 boiled egg (65 cal), 100 g of wheat bread (265 cal), 20 g buttered on top (750*20/100=150 cal) and a piece of Russian cheese on top 20 g (371*20/ 100=74.2 cal) and tea with sugar (290*15/100=43.5 cal). This is already 65 + 265 + 150 + 74.2 + 43.5 \u003d 597.7 cal based on this table and given that calories per 100 g of the product are given there.
For lunch, you can eat a pie with onions and eggs with dried fruit compote. Also, all kinds of desserts are best eaten before 12-00. For lunch, you can allow delicious main courses such as or sole fish . From the first courses you can eat green borscht or lentil soup . For an afternoon snack, all kinds of snacks and nuts are suitable. Dinner is best made light. It can be cottage cheese with herbs, light chinese cabbage salad , green tea or a healthy rosehip decoction, kefir.
But this video talks about the wrong diet and clearly shows what such a fasting diet leads to, which organs suffer and what diseases can appear!
To determine the energy balance, it is necessary to know the energy value (calorie content) of food products, and correctly measure it and our energy costs. The energy value of food is calculated according to the corresponding coefficients established on the basis of determining the combustion in the body of nutrients - proteins, fats and carbohydrates. Today we will tell you what the daily norms of human nutrition are, and on the basis of what they are established.
At present, the chemical composition and energy value of all basic foodstuffs have been studied.
Energy balance in the daily diet
Energy costs are made up of unregulated and regulated by the will of a person energy costs. The unregulated types of energy costs include energy consumption for specific dynamic action (SDA) and basal metabolism (in a state of complete rest). For a person weighing 70 kg, the basal metabolic rate averages 4.1868 kJ per 1 kg per hour, or 7117.56 kJ / day (1 kcal is equal to 4.1868 kJ). The basal metabolism depends on sex and age. With age, the basal metabolic rate decreases. In men, it is 5-10% higher than in women.
Under the influence of food intake, energy consumption increases, which is due to increased oxidative processes. With a mixed diet, the basal metabolism increases by 10-15% per day, its greatest increase (by 30-40%) is caused by the intake of proteins, while when taking fats, the metabolism increases by 4-14%, carbohydrates - by 4-7% .
Regulated energy costs are determined by its consumption during the performance of muscular work.
How are daily nutritional allowances determined?
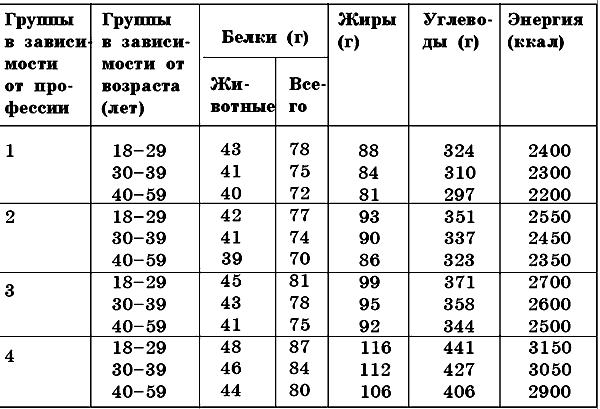
When organizing nutrition and planning the required amount of nutrients and energy, they are guided by the recommendations developed by the Institute of Nutrition of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences. These recommendations take into account age, gender and character labor activity to establish the daily norms of human nutrition. The normalization of the physiological need for nutrients and energy of the adult working population is carried out according to 5 groups of labor intensity, depending on daily energy costs, the nervous tension of the labor process and other features.
A prerequisite for balanced daily human nutrition is to ensure the correct and reasonable ratio of the main food and biologically active substances - proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals - taking into account age, gender, nature of work, etc.
Daily human nutrition
Depending on the functional purpose, nutrients are divided into predominantly energy (fats, carbohydrates), predominantly plastic (proteins, a number of minerals, water) and predominantly catalytic (vitamins, trace elements). Taking into account the criterion of obligation, nutrients are differentiated into replaceable and irreplaceable. Non-essential nutrients include carbohydrates and fats, and essential nutrients include the 12 essential amino acids, the 3 essential polyunsaturated fatty acids, all vitamins (16) and most minerals (60).
The balance of proteins, fats and carbohydrates in modern diets should be established taking into account their energy value, while their ratio will look like 1: 2.7: 4.6 (kcal), otherwise for each protein calorie there should be 2.7 fat and 4.6 carbohydrate calories.
As already mentioned, quite often the cause of obesity and the appearance of excess weight is overeating or malnutrition. In order for nutrition, including medical nutrition, to be rational, many parameters should be taken into account - such as gender, age, height, weight, nature of work, etc.
The intensity of labor and other physical exertion on the body is a very important factor in making the right diet. Experts distinguish five main groups of people depending on the nature of their work activity.
The first group includes knowledge workers. These are business leaders, medical workers (except for nurses, nurses and surgeons), educators and teachers (except for sports), workers in science, literature, secretaries, dispatchers, clerks, etc.
To the second - workers of light physical labor, whose activities are associated with small physical activity. These are agronomists, livestock specialists, garment workers, workers in the service sector, communications, the watch industry, nurses, orderlies, salesmen of department stores, teachers, trainers, etc.
To the third - workers of average on gravity of work. These are machine operators, surgeons, shoemakers, transport drivers, workers Food Industry, public catering, railway workers, printers, crane operators, etc.
To the fourth - workers of heavy physical labor. These are builders, miners engaged in surface work, machine operators, workers Agriculture, carpenters, riggers, etc.
To the fifth - workers of especially hard physical labor. These are miners engaged in underground work, steelworkers, masons, concrete workers, excavators, loaders, etc.
With regard to age categories, there is a division into three groups: 18-29, 30-39 and 40-59 years. This takes into account the average body weight for men and women separately. The average body weight of men is 70 kg, women - 60 kg.
It is known that the need for energy in women is 15% lower than in men.
It is also important to take into account climatic conditions. Residents of the northern regions require 10-15% more energy than residents central regions, and southerners are 15–20% more than residents of central regions.
The physical norms compiled by specialists, of course, do not take into account all possible factors, therefore, when compiling a therapeutic diet for obesity, it is necessary to undergo additional consultation with a specialist, especially if a person suffers from other ailments. All this must be taken into account. Some people may have their own taste preferences, healthy or unhealthy, they may be allergic to any food product. In this regard, the physiological norm of nutrition will depend on both these and other factors, but you still need to focus on the norms proposed by specialists (Tables 6 and 7).
Table 6Physiological daily norm of proteins, fats, carbohydrates and energy for an adult able-bodied manTable 7Physiological daily norm of proteins, fats, carbohydrates and energy for an adult able-bodied woman
In order to properly compose a diet, choose the necessary products, you need to take into account the nutritional properties of each product, its calorie content and saturation with vitamins and minerals. Get rid of excess weight it is possible only by making a strict calculation of the calorie content of all products that will be included in the menu. You can reduce the caloric content of the diet at the expense of fats and carbohydrates, replacing foods that contain them in excess with others that are no less useful (Table 8).
Table 8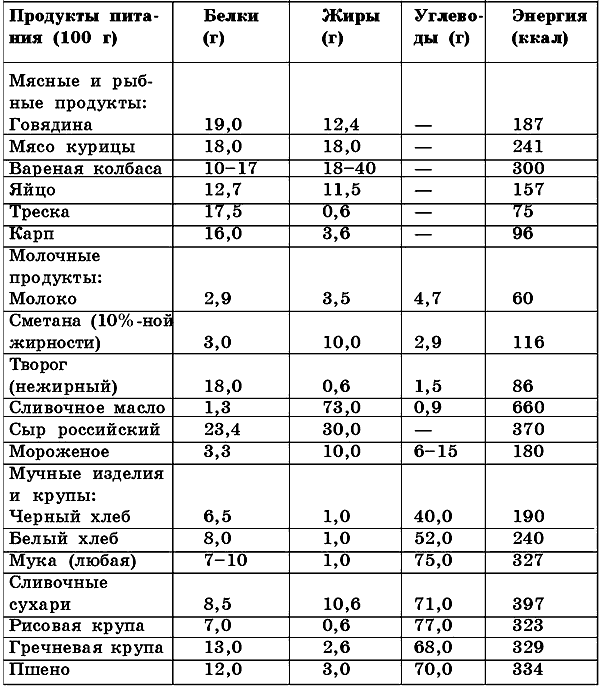
continuation)and energy in staple foods
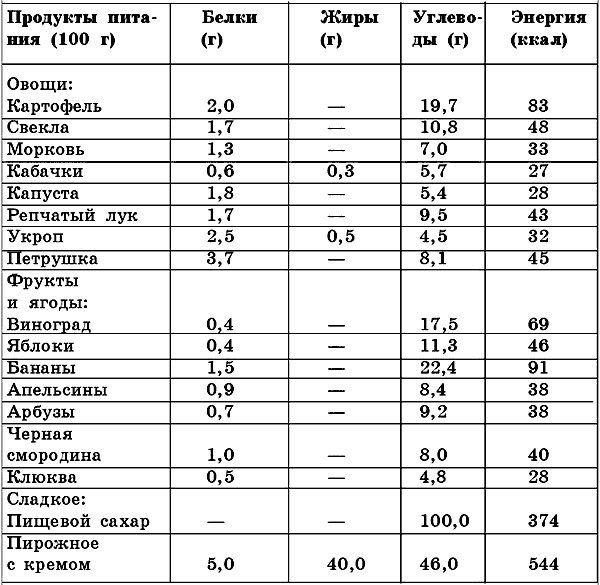
Some products contain a certain amount of cholesterol. With obesity, it is necessary to exclude from your menu dishes abounding in them. These are meat and fatty dishes. There is no cholesterol in vegetables and fruits, just as there is no cholesterol in flour products and cereals. However, the latter foods are also not recommended for overweight.
The amount of cholesterol in staple foods is as follows (per 100 g of product).
I. Vegetables, fruits and berries:
- potatoes, beets, carrots, zucchini, cabbage, onions, dill, sorrel, apples, bananas, oranges, watermelons, cranberries, black currants, etc. - 0 mg.
II. Flour products and cereals:
- black bread, flour (any), creamy crackers, rice groats, millet, buckwheat groats, etc. - 0 mg.
III. Sweet:
- food sugar - 0 mg;
- cake with cream (depending on the cream) - 50-100 mg.
IV. Dairy products:
- milk - 10-15 mg;
- yogurt - 8-30 mg;
- cream - 20-40 mg;
- cottage cheese (fatty) - 20-40 mg;
- cottage cheese (low-fat) - 40 mg;
- Russian cheese - 80–90 mg;
- sour cream (10% fat) - 100 mg;
- ice cream - 20-120 mg;
- butter - 180 mg.
V. Meat and fish products:
- egg (protein) - 0 mg;
- cod - 30 mg;
- boiled sausage (depending on the types of meat used) - 0-40 mg;
- turkey - 63 mg;
- veal - 64 mg;
- chicken meat - 73 mg;
- duck - 78 mg;
- lamb - 80 mg;
- beef - 86 mg;
- herring - 95 mg;
- carp - 96 mg;
- lean pork - 100 mg;
- shrimp - 200 mg;
- egg (yolk) - 225 mg;
- liver - 270 mg;
- salmon caviar - 300 mg.
As can be seen from the proposed list of products, the largest number cholesterol is found in fish caviar, which, despite this, is the most valuable product, because it contains many useful substances. If caviar is eaten in small quantities, correlating the total calorie content of all foods on the menu and their cholesterol content, then caviar will not do much harm, especially if there is one of the fruits for dessert that helps lower blood cholesterol levels and generally improves digestion and absorption of nutrients.
Vitamins and minerals, which are found in abundance in many fruits and vegetables, have similar biological activity. They improve digestion, remove toxins from the body, reduce the level of fats, carbohydrates and cholesterol in the blood, increase a person's vitality.
Experts have identified the daily requirement of the body for vitamins. The norm of consumption of vitamins by an adult per day is as follows.
Retinol (vitamin A) - 10-15 mg.
Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) - 20-30 mg.
Thiamine (vitamin B1) - 0.14 mg.
Riboflavin (vitamin B2) - 0.19 mg.
Pyridoxine (vitamin B6) - 0.17 mg per 1000 kJ.
Folacin (vitamin B9) - 200 mcg (for pregnant women and patients - 400 mcg).
Cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12) - 3 mcg (for pregnant women - 4 mcg).
Niacin, or nicotinic acid (vitamin PP), - 1.57 mg.
Tocopherol (vitamin E) - 10 mg (for children 3-15 mg).
Phylloquinone (vitamin K) - 0.2–0.3 mg.
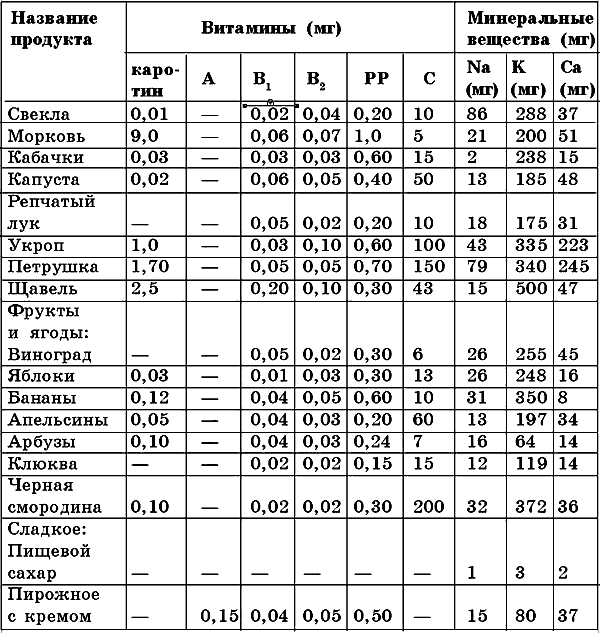
Minerals are also necessary for the body to build cells and tissues, for the normal functioning of enzyme systems. These substances are divided into macronutrients and micronutrients. The former include sodium, phosphorus, calcium, magnesium, iron and potassium. To the second - silicon, fluorine, iodine, nickel, chromium, molybdenum, cobalt, manganese, zinc, copper, etc. The need for macroelements is measured in grams and milligrams, and for microelements it is tens and hundreds of times less. For example, table salt (sodium chloride) requires 10-15 g per day, calcium - 800-1000 mg, iron - 15 mg. The number of trace elements per day will be much lower, so a full and varied diet may well compensate for the human body's need for these substances (Table 9).
Table 9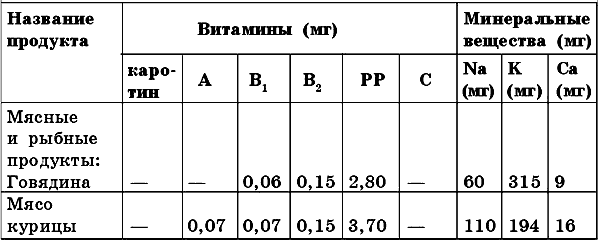
continuation)substances in staple foods (based on 100 g of product)
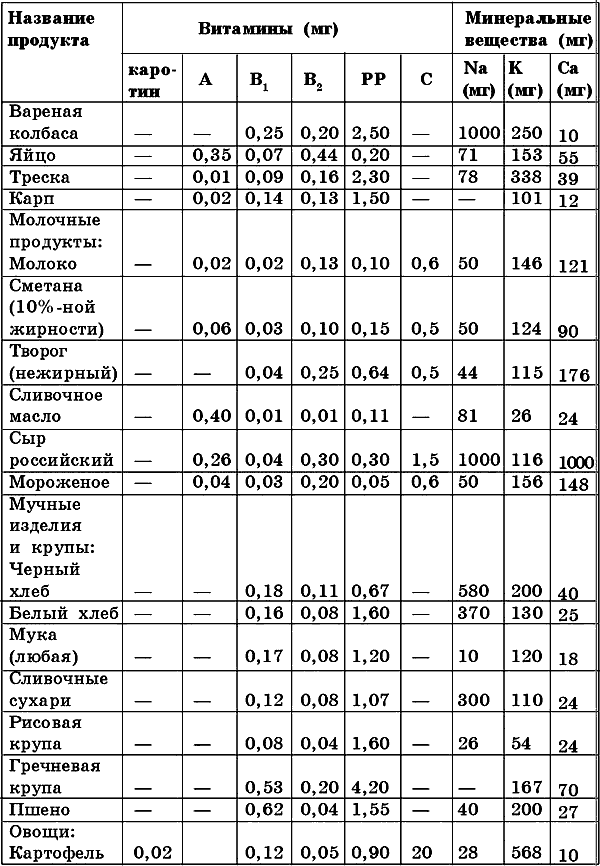
continuation)substances in staple foods (based on 100 g of product)
In dietology, such a concept as a "bread unit" was introduced. She combined the content of carbohydrates in the product and the number of calories. As you know, to get rid of excess weight, you need to limit the intake of carbohydrates and reduce the calorie content of food. To simplify the calculations of the content of carbohydrates in products and their calorie content, they resort to the "bread unit" system, or XE, which is international. When buying food in the store, you can, based on the instructions on the label, determine the carbohydrate value of the product. For 1 XE conditionally take 12 g of carbohydrates, which are contained in 25 g of black bread. This is a regular, portioned piece of bread 1 cm thick.
When compiling an individual diet, it is necessary to take into account the amount of XE in the product. Foods containing carbohydrates and fats should be evenly distributed throughout the day, while total XE should not exceed the prescribed norm.
Per day healthy man can consume more than 22 XE, but the patient needs a consultation with the attending physician, after which, depending on the nature of the disease associated with obesity, an individual rate of XE consumption per day will be established.
Each product contains a certain number of bread units. 1 XE is contained in the following products (product weight indicated).
I. Lump sugar and granulated sugar - 10 g.
II. Bakery products:
- white bread - 20 g;
- black bread - 25 g;
- dry biscuits (crackers), crackers, breadcrumbs - 15 g.
III. Pasta:
- noodles, vermicelli, horns, pasta - 15 g.
- buckwheat, corn flakes, semolina, flour (any), oatmeal and pearl barley, oatmeal, millet, rice - 15 g.
V. Potatoes:
- chips - 25 g;
- fried - 35 g;
- boiled - 65;
- puree - 75 g.
VI. Dairy products:
- ice cream - 50–65 g;
- milk, kefir, cream - 200 ml.
VII. Fruits and berries (with pit and peel):
- banana, grapes, persimmon - 70 g;
- figs - 80 g;
- cherry, pear, plums, apple - 90 g;
- melon - 100 g;
- apricots, kiwi, mango - 110 g;
- gooseberries, peach - 120 g;
- quince, pineapple, blackberry, blueberry - 140 g;
- raspberry, tangerine, orange - 150 g;
- strawberries, wild strawberries - 160 g;
- pomegranate, grapefruit - 170 g;
- watermelon - 270 g.
VIII. Other products:
- corn - 100 g;
- kvass, beer - 250 ml.









