In order to draw the solar system, you must first know and study the solar system well, and then take white clean paper, multi-colored pencils, original picture solar system (like a still life) and start with the contour of the planets and the sun, rearrange the planets correctly and then paint them. There are already very good graphic shots above, so I have attached only pictures from which you can start drawing, following my instructions.



If you need a drawing with all the planets around the sun, then the user Txajan showed how to draw the solar system in full. I want to suggest how to draw the solar system from another review.



Very often at school they are given the task of drawing the solar system. For this purpose, we need colored pencils and a sheet of paper.
First of all, draw the Sun.

Then we proceed to the very first planet Mercury. It is a small ball and a gray-brown color.


Mercury is followed by a green-blue Earth with a gray dot of the Moon.

Then we draw red Mars. It is larger than Mercury, but smaller than Earth.

The gray shadow behind Mars symbolizes the asteroid Belt.

Next comes the striped orange-white Jupiter.

Then we draw a yellow Saturn.

And behind him - the blue-blue planet Uranus.


Well, the last planet is a tiny brown Pluto.

In order to draw our solar system with pencils step by step, we will need the following items.
First we need - Pencils (multi-colored), White paper and most importantly - Photo - scheme.
Below I have attached a photo - diagram for your convenience. draw our solar system.
First you need to draw the orbits of the planets (as in the diagram.)

Then we start drawing general form planets of the solar system.
At the beginning you need draw the sun.
After that you need draw the planet Mercury.
Then you need draw the planet venus.
Then we start draw the planet mars.
After Mars draw the planet Jupiter.
After you draw the planet Jupiter, start draw the planet saturn.
After Saturn draw the planet Uranus.

After you have drawn the planets, start drawing comets and asteroids (as in the diagram).

So we continue, as in the diagram.


In the end, we start painting as in the diagram below and we get this beautiful picture solar system.

draw the solar system There are many ways to go to physics class.
The main principle of drawing the solar system is to show the sun in the center of the system, and the planets that revolve around the sun in their orbits.
Mercury is closest to the sun in the solar system, followed by the planet Venus, then our planet Earth, then comes Mars, after Mars Jupiter, then Saturn, Uranus, Neptune and Pluto.
You can draw the orbits of the planets of the solar system simply by placing circles around the circle-sun or by drawing them in the form of ellipses.
The planets themselves are drawn in the form of circles, it is desirable to observe the size of the circles in accordance with the size of the planets, showing their approximate sizes in relation to each other.
Solar system drawing You can just draw with a pen or felt-tip pen, or you can color it. making the background dark.



The solar system is the Sun and other space objects that revolve around this star.
Drawing a solar system is not so difficult. You just need to know the placement of certain objects / planets, their sequence and name.
Draw the solar system with a pencil like this:






Drawing the solar system with a pencil is not so difficult. To do this, you need to designate the center of the system - the sun. can draw big circle and flames from it. Then we draw a circle and a circle-planet Mercury on it. Draw another circle and next planet On him. So we depict all the planets of the solar system.
All drawings are relatively easy, so everyone will be able to copy them.
The most important and main tool - an assistant in drawing our solar system - is a compass! Or, in extreme cases, an mp3 disc. It will help to draw both the Sun and all planetary orbits.
We start, perhaps, with the largest circle (this is our Sun), draw the lines of orbits, draw the planets with a compass, and depict the stars under the guise of many points.

I propose to draw solar system pencil in stages as follows:

Drawing steps:
1) We start drawing with the image of the sun and nine lines around, on which we will place the planets;
2) We begin to draw the planets with circles;
3) Draw Saturn with a circle around meteorites;
4) We finish drawing with Plato;
5) We hatch the planets with a pencil.
In this lesson you will learn how to draw space and planet. .
Step 1.
First we will draw the starry sky. Create a new document and fill it with black. I set the size of the new document to 1600x1200 so that it can later be used as desktop wallpaper. Duplicate this layer (ctrl+ J) . Next, apply a noise filter to the new layer. Filter - Noise - Add Noise(Filter - Noise - Add Noise). Set the noise amount to 10%, Gaussian distribution, and check Monochrome.

Step 2
Next, go to the menu item Image > Adjustments > Brightness & Contrast(Image > Adjustment > Brightness/Contrast) and set the Brightness 30 and Contrast 75 . Now the noise is more like stars.

Step 3
Now let's add bigger stars. Duplicate the previous layer with stars (ctrl+ J) and change its brightness and contrast Image > Adjustments > Brightness & Contrast(Image > Adjustment > Brightness/Contrast) set the Brightness 100 a Contrast 50

Step 4
Click (Ctrl+T) and make a layer with big stars approximately twice as much. Hold Shift to transform the layer proportionally. Click (Ctrl+L) to bring up the Levels window. Set the parameters as in the picture to increase the contrast. (In my case, I had to set the parameters opposite to those of the author 0 , 1.00 , 20)

Step 5
Set the blending mode for the layer to Screen (Lightening). To avoid the echo effect (overlay effect), press Ctrl + T and rotate the layer 90 degrees (while holding the Shift while rotating the layer, the layer will be rotated in 15 degree increments). Use this technique when rotating.

Step 6
Take a soft rubber band with a diameter of about 20-30 px and start erasing our stars on both layers. Try to create various forms in all directions to make our stars look more natural. Also remember that there should be more black space than space with stars, and more small stars than big ones.

Step 7
Try to create some star regions with the tool Clone Stamp(Stamp) using a brush with soft edges. You have to decide for yourself where to place the clouds with stars, and where to leave empty space. Use your imagination and you will succeed.

Step 8
Let's add glow to the stars. Duplicate the big stars layer. Apply a filter Filter > Blur > Gaussian Blur(Filter - Blur - Gaussian Blur) with a Radius of approximately 10 px and change the Color Blending Mode to Linear Dodge(Linear Dodge). Press Ctrl+U and colorize the glow of the stars (I set Hue ( hue) by 230). Repeat this step several times to make star Light more expressive.

Step 9
And now we will create the rest of the details of our space landscape: huge stars, stardust and colorful nebula. Create a new layer and set the blend mode for the layer Linear Dodge(Linear Dodge) and fill it with black. Further Filter - Render - Lens Flare ( Filter - Rendering - Highlight ) . I used a 35mm lens type. Create a couple more big stars by changing the location of the center of the highlight and the brightness of the highlight. Use different colors for each of the stars, this will give some variety. big picture(most easy way to do this - press Ctrl+U and change Hue ( Color tone)).

Step 10
Create a new layer to create the stardust. Install opacity(layer opacity) to 25% and change the blend mode for the layer to Screen(Lightening). Select any brush with soft edges and set it up as shown. I used texture for the brush Confetti, this is one of the standard Photoshop textures. Now that we've set up our brush, let's paint our stardust. blue color (#ced0f1).

Step 11
And now let's create a multi-colored nebula. Create a new layer, take a soft round brush and paint a cloud like mine. It's quite easy: first draw the blue base, then the red area, and finally the yellow and white. Apply a filter to the nebula layer Filter - Blur - Gaussian blur(Filter - Blur - Gaussian Blur) with a radius of 50 px.

Step 12
Now let's give our nebula the shape of clouds. To do this, create a new black layer and apply a filter to the layer. Filter - Render - Clouds ( Filter - Rendering - Clouds). Change the blend mode for the layer to overlay(Overlap). After that duplicate the cloud layer (ctrl+ J) .

Step 13
Select the nebula layer and edit it opacity(layer opacity) to 55% and the blending mode for the layer to Screen(Lightening). Find the best place for your nebula and move it there.

Step 14
Well, we have finished drawing the starry sky. Now let's create a planet. Find a stone texture for your future planet. I used this one from SXC. http://www.sxc.hu/photo/1011795
You can also use your own texture.

Step 15
Open the texture image. Let's resize the canvas to give the texture a square shape. Image- canvas size ( Image - Canvas Size ) . Set the same values for height and width. Use the tool Clone Stamp(stamp) to fill empty seats texture. Also remove too dark spots with the same tool. Further Edit - Define Pattern(Editing - Define pattern). Save the pattern under any name you like. After that, you can close the image with the texture.

Step 16
Create a new document (ctrl+
N)
size 1600x1600 pixels. Fill it with black. Using the tool Elliptical Marquee Tool ( Selection ”Oval area” )
create a circle selection. To make the circle even and fit into the square, press Shift +
ctrl and without releasing these keys approximately from the center of the square, start drawing a selection. After you draw the selection, fill it with the pattern we created in the previous step. Image -
Fill- Contents: Pattern
(Editing - Fill - Use: “Pattern”). And select the pattern we created for the fill.

Step 17
Apply the filter without deselecting Filter - Distort - Spherize ( Filter - Distort - Spherize ) Amount 100% ( Degree 100%. ctrl + F to repeat the last applied filter.

Step 18
Duplicate the planet layer (Ctrl + J) and fill the circle with light blue (#455571). This will be the atmosphere of the planet. You can use any other color for this.

Step 19
Duplicate this layer and fill it with black. This will be the shadow of the planet. Now select the atmosphere layer, double click on it to bring up the window Layer style (Layer style). Apply the following layer styles to the atmosphere layer:
Step 20
Move the shadow layer above the atmosphere layer ( ctrl +] -
layer up )
(ctrl +[ -
layer down )
. Apply a filter to the shadow layer Gaussian blur
(Filter - Blur - Gaussian Blur) Gaussian Blur (Filter - Blur - Gaussian Blur) with a radius of 75 px.

Step 21
Press Ctrl+T and transform the shadow: increase its size and move it a bit to the top left corner. I chose this position for the shadow because I'm going to place the planet in the top left corner of the painting and the light comes from the big star, which is in the center.

Step 22
Select the atmosphere layer and set the layer blending mode Screen(Lightening), so we will see the surface of the planet. I don't like the brightness and contrast of the planet, so I reduced opacity( layer opacity ) up to 33%. After that I duplicated the planet surface layer and set the layer blending mode to soft light(Soft light). Also I changed opacity shadow layer by 90%.

Step 23
Now we need to copy our planet to the starry sky. For this
disable background(background) by clicking on the eye icon
responsible for the visibility of the layers. Shift+Ctrl+E to merge the visible layers. Now copy the planet to a file with starry sky and place it in the corner of the document. In the end, I added a glow to the planet.

Conclusion
That's actually all!!!
Good luck and patience in creating your space landscapes.
Space attracts not only scientists. This eternal theme for drawing. Of course, we cannot see everything with our own eyes. But the photos and videos taken by the astronauts are amazing. And in our instructions we will try to depict space. This lesson is simple, but will help the child figure out where each planet is.
You will need: a sheet of paper; pencil; eraser; compass;
Step 1
Basic circle
First draw a big circle on right side sheet. If you don't have a compass, you can trace around a round object.
Orbits
Orbits of planets that are at the same distance depart from the center. 
central part
The circles are getting bigger. Of course, they will not fit completely, so draw semicircles.  The orbits of the planets never intersect, otherwise they will collide with each other.
The orbits of the planets never intersect, otherwise they will collide with each other.

We finish drawing the orbits
The entire sheet should be covered with semicircles. We know only nine planets. But what if there are also cosmic bodies in distant orbits that move along the most distant orbits.

Sun
Make the central circle a little smaller and circle it with a thick line so that the Sun stands out from the rest of the orbits.

Mercury, Venus and Earth
Now let's start drawing the planets. They need to be placed in a certain order. Each planet has its own orbit. Mercury revolves around the sun itself. Behind him, in the second orbit, is Venus. The third is the Earth.

Mars, Saturn and Neptune
Earth's neighbor is Mars. It is slightly smaller than our planet. Leave the fifth orbit empty for now. The next circles are Saturn, Neptune. These celestial bodies are also called giant planets, as they are ten times larger than the Earth.

Uranus, Jupiter and Pluto
Between Saturn and Neptune is another big planet- Uranus. Draw it on the side so that the images do not touch.
 most big planet The solar system is considered to be Jupiter. That is why we will depict it on the side, away from other planets. And on the ninth orbit, add the smallest celestial body - Pluto.
most big planet The solar system is considered to be Jupiter. That is why we will depict it on the side, away from other planets. And on the ninth orbit, add the smallest celestial body - Pluto.

Rings on Saturn
Saturn is known for its rings that have appeared around it. Draw several ovals in the center of the planet. Draw rays of different sizes that depart from the Sun.

planetary surfaces
The surface of each planet is not uniform. Even our Sun has different shades and black spots. On each planet, depict the surface using circles and semicircles.

Draw fog on the surface of Jupiter. This planet often experiences sandstorms and is overcast.

The last details are concentric circles on the Sun. On some planets, draw a shadow, separating it with a semicircle. You can also draw near the Earth its satellite - the Moon.

Coloring
space in space dark blue. The sun is yellow, Mercury is grey, Venus and Jupiter are brown. The earth is green and blue. Mars is red, Neptune is green, Saturn is sandy and its rings are white or light blue as they are icy. Uranus is blue-blue and Neptune is grey-black. You can also add other details like stars, comets and asteroids.

INTRODUCTION
In this tutorial, we will look at planetoids (asteroids) and planets with minimal or zero atmospheres, and how the absence of an atmosphere affects these objects (or rather, how the absence aerial perspective can distort our stable artistic perception!). Most importantly, you will learn in detail how to draw space. (Fig. 01a).
Knowledge of the atmosphere, or lack of it, explains how correctly and realistically we imagine an Earth-like (blue) environment compared to alien, unexplored climates (for example, a methane-rich atmosphere that colors the sky in green color). In this regard, we will focus our attention on our satellite - the Moon - as a base to which we will apply other exotic habitats.
On fig. 01b note the numerous details from the foreground to the middle of the image, and how the most dark shades distributed evenly. Usually in the atmosphere dark colors"brightened", and objects at far distances appear brighter.

Click on the image to view the image in full size and 100% quality.
Planetoids with minimal or no atmosphere would be like distant landscapes (at sea level, with amazing clear visibility up to 4.67 km along the curve of the earth). But first of all, let's talk about the building blocks of the environment of relative abstraction and Zen technique (Note: you can skip these basics and come back in another chapter).
ENVIRONMENTAL BASICS
Zen Buddhism says "Form is emptiness, Emptiness is form." The fact is that our ancient ancestors studied and analyzed the universe in the smallest details, and thus concluded that everything can be simplified to a circle (Fig. 02). The practice of meditation in Zen Buddhism is different types and forms. In particular, the Zen Circle, also known as "Enso" (Enso), speaks of emptiness and form as interdependent things - its mantra reads "Form is emptiness, Emptiness is form." Seen through the lens of Zen Buddhism, one can say of Enso (Fig. 02) that "The circle becomes the universe."

By this logic, it can be assumed that the building blocks of the universe originated from the square, triangle and circle (Fig. 03). This concept was particularly well received and expounded by the monk Gibon Sengai (1750-1837). If you put all these elements together, they radically change the shape of the great circle, which is the shape of the universe - giving shape to the void (Fig. 04).

Click on the image to view the image in full size and 100% quality.

SHAPE - SQUARE, TRIANGLE, CIRCLE
In the east, symbolism is very often used, for example, the Japanese use the following signs and their meanings:
X - cross = "bad" or "cancel"
∆ - triangle = "average value"
Ο - circle = "good" or "affirmative"
□ - square = "excellent" or "bull's eye!"
NOTE: The circle is the equivalent of a check mark (tick) which means "correct" and is therefore used to convey an action. However, when Japanese products have made their way into Western markets, these symbolisms are often ignored (for example, PlayStation joysticks have "X" and "Ο" buttons for consumers in Europe and North America).
It would probably make more sense to use these geometric symbols found in common Japanese instructions (or PlayStation joysticks) to draw or create life (art and new words). In addition, when you bring the square, triangle, and circle into perspective, they immediately form useful and familiar shapes. Therefore, these shapes can be rearranged to form a cube, a sphere, and a pyramid (figs. 05a and 05b).


Click on the image to view the image in full size and 100% quality.
If we talk about the use of these figures in conditions external environment, then they can equally be applied as mountains, planets, rocks and buildings. Each shape will have light and dark side, which convey a simple readable form. If we go even further, in reality there will also be a main shadow, or an area of high contrast where the edge of the figure breaks off. The reflected shadow usually falls on the area farthest from the main shadow (Fig. 06); for example, the main shadow is an edge (line) absolutely perpendicular to the light itself.

Click on the image to view the image in full size and 100% quality.
In general, these forms can be applied to both organic shapes (characters/creatures) and inorganic ones (buildings/environments), especially links (which can best describe soft and hard shapes) (Figure 07).

Click on the image to view the image in full size and 100% quality.
COMPOSITION AND ATMOSPHERE (… or lack of atmosphere)
Using the same basic figures, I want to visually demonstrate to you the atmospheric perspective (Fig. 08).

Click on the image to view the image in full size and 100% quality.
On fig. 08 I used the same objects to create buildings for the scale of people. Note that all objects in shadow have the same shade tone as any of the large objects that stand in the way of the light source. In terms of perspective, if you have two objects of the same height, the farther away they are, the smaller they need to be.
Your task: Try to repeat all this using similar objects. Sometimes such a simple task can be challenging in itself, but at the same time very useful in learning visualization, form and lighting - even for experts (some experienced artists achieved a lot without learning the basics, but it is this lack of knowledge of the basics that distinguishes them from professional artists) (Fig. 09).

Click on the image to view the image in full size and 100% quality.
On fig. 09 Notice how dull and unrealistic the picture looks. Without atmospheric perspective and color (minimum), drawing lunar landscapes can be quite a nuisance! In fact, you just need to intelligently add a few colored elements, whether it be an image of the earth, local objects created by man, etc. In this case, I colored the sphere gold (also applied to the Apollo Lunar Modules!).
SURFACE OF THE MOON
Finally, having dealt with the basics of form and composition in environment, you can move on to the most important thing in this lesson!
First of all, they say that the moon has no atmosphere. There are traces of gases such as radon, or micrometeorites. In addition to this, the solar wind can charge (photoelectric effect) layers of lunar dust, which can be electrostatic flying dust. Cosmic radiation, together with solar flares and solar wind, as well as periodic collisions of micrometeorites, form extremely aggressive conditions for existence!
With a closer study of the surface of the moon, we will see (Fig. 11):
- gray surface
- a layer of rock fragments covering most the surface of the moon, also known as "regolith";
- moon dust.

Click on the image to view the image in full size and 100% quality.
On fig. 12 we see:
- Dark areas known as "maria/mare" ("seas"), formed from hardened lava;
- Terrae ("earth"), which includes the mountainous areas of the moon, they are lighter in color and have craters on a hill. They represent areas between various seas, but are not officially used in lunar terminology;
- A very thin layer of the atmosphere (contrary to popular belief) that cannot resist solar radiation, wind and cosmic radiation; thus, it is necessary to depict a minimal atmosphere, for example, using a thin layer of invisible haze;
- The temperature varies from 127 to 173 degrees Celsius and constantly changes depending on the position of the sun; for comparison, a regular deep frying pan fries at a temperature of 180-200 degrees, i.e., in simple terms, on a sunny day on the surface of the moon, it is hot enough to cook a hard-boiled egg, but not hot enough to make crispy chips!

Note: The upper layer of the moon's surface consists mainly of:
- regolith - a layer of rock fragments lying on a bedrock about 5 m thick. V open areas(Fig. 10) (Italian: Maria - large, dark, basaltic fractures on the surface of the moon, resulting from volcanic eruptions) and 15m. in more elevated areas (Fig. 10 shows how similar the terrestrial and lunar regoliths are);
- lunar dust - consisting of dust particles that are in constant motion; when heated, it can turn into electrostatic flying dust;
- seas (maria) - dark spots different forms, also known as capes (dorsa, dorsum, promontorium).

Click on the image to view the image in full size and 100% quality.
Well .. While my movie is loading, I'm doing a lesson in drawing space .. It might come in handy.
How to draw space with a pencil step by step
Step one.
We draw a round shape for the planet and the outlines of the landscape.
Step two.
Let's correct the contours of the planet and its satellite. In the foreground we draw two little men, these are astronauts sent to the moon.

Step three.
Let's add strokes.

Step four.
Let's draw a starry sky. Or, to be more precise, this outer space. in the middle lunar landscape draw some craters.

Step five.
And it remains to add some shadows. In the end it turned out like this space picture:

How to draw the Earth with a pencil step by step
Step one. Drawing a circle by hand is very difficult. First we need two squares, divided in half, in order to fit the colo into them. Of course, you can take a compass and draw a kolo. But this is not the king's business.  Step two. As mentioned above, we make the outline of our planet, draw four arcs at the corners of the square.
Step two. As mentioned above, we make the outline of our planet, draw four arcs at the corners of the square.  Step three. Now it will be easier to draw even circle. We combine the arcs so that everything turns out as clear as possible.
Step three. Now it will be easier to draw even circle. We combine the arcs so that everything turns out as clear as possible.  Step four. Now we sketch on our ball all the continents, oceans, islands and peninsulas. Anything that will fit and be noticeable.
Step four. Now we sketch on our ball all the continents, oceans, islands and peninsulas. Anything that will fit and be noticeable.  Step five. We remove the auxiliary lines. We stumble around the planet with dots - an image of distant stars, move with a pencil, depict the cosmos so that the planet does not look lonely.
Step five. We remove the auxiliary lines. We stumble around the planet with dots - an image of distant stars, move with a pencil, depict the cosmos so that the planet does not look lonely. 
How to draw the planets of the solar system with a pencil
Step one
Draw the orbits of the planets. Their shape is an ellipse close to a circle. But, if you look from one point, then visually we see not circles, but arcs, parts of ellipses. Such as in the picture. On the lines we outline the positions of the planets.

step two
We draw circles - planets. We start with small Mercury, then Venus and the Earth are larger, again a small circle is Mars and further, as in the figure. In the lower left corner we show the edge of the Sun.

Step Three
Erase the auxiliary lines - the axes of the circles. Let's make the orbits brighter.

Step Four
Let's add others celestial bodies: comets, asteroids. Let's draw "rings" to the major planets.

Step five
Let's do the shading. With it, we must turn our circles into a sphere. Remember that we have the Sun in the center, and light falls from its side. But the opposite side of the planet will be darkened. The result should be something like this:

How to draw an astronaut with a pencil step by step
There are four steps ahead.
Step one.
In the upper part of the sheet we place a round large head. She's big because she's wearing a helmet. Let's go down two curved lines is the outline of the body. We will draw an astronaut in zero gravity. And this immediately sets his position. Let's draw the contours of the arms and legs. There is a belt on the suit. Let's outline a backpack behind our shoulders.

Step two.
We begin to draw the details: a helmet, fingers, all sorts of bells and whistles on the "suit". And all the elements are quite large.

Step three.
Draw an opening for the eyes on the helmet, make it voluminous. Let's start drawing shoes. Let's show the pocket-bag on the belt. Look carefully at the picture and fill in the missing on your sheet. Rivets, folds on the fingers and more.

Step four.
On the belts we will show horizontal shading. Let's draw the shoes: a pattern on the sole, a clasp. On the hip of the astronaut is a small electronic device. Now let's outline the main elements of our drawing. Almost done. You can “revive” our hero with the help of hatching, or give color with the help of paints!

How to draw a space rocket with a pencil step by step
Step one. Our rocket is not just some kind of apparatus with an engine, but a whole spaceship. We draw two oval figures - this is the hull of the ship. At the bottom, we will notice one wing of the rocket, and behind - the tail.  Step two. We connect the ovals. The structure of the rocket, its structural parts have complex shape which does not make sense to describe. Therefore, try to repeat as you see in the picture, or you can come up with your own rocket.
Step two. We connect the ovals. The structure of the rocket, its structural parts have complex shape which does not make sense to describe. Therefore, try to repeat as you see in the picture, or you can come up with your own rocket.  Step three. The ship should have many different parts on the hull, plates, guns, portholes.
Step three. The ship should have many different parts on the hull, plates, guns, portholes.  Step four.
Step four. 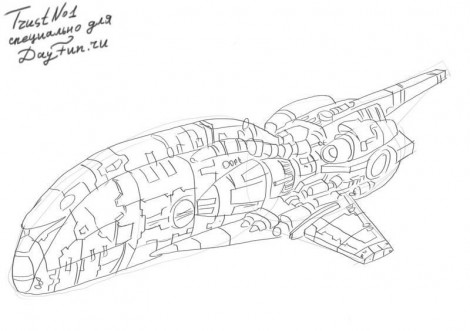 Step five.
Step five. 
How to draw a moon rover with a pencil step by step
Step one. Let's divide the device into structural parts, depicting them on paper in the form of rectangles.  Step two. Let's sketch a sketch of an astronaut sitting in a car.
Step two. Let's sketch a sketch of an astronaut sitting in a car.  Step three. Add a small antenna in front of the machine, outline the person behind the wheel in more detail.
Step three. Add a small antenna in front of the machine, outline the person behind the wheel in more detail.  Step four. Let's remove the auxiliary lines and outline the contours more clearly.
Step four. Let's remove the auxiliary lines and outline the contours more clearly.  Step five. To show the effect of movement, we will make shadows under it, and add hatching to the wheels, the astronaut and other parts. Here:
Step five. To show the effect of movement, we will make shadows under it, and add hatching to the wheels, the astronaut and other parts. Here: 
How to draw a spaceship with a pencil step by step
Step one. Draw the pattern with geometric shapes for the ship, we will display the hull and places for the engines.  Step two. Let's draw jet turbines, tweak the lines of the hull a little and add a small cannon under it.
Step two. Let's draw jet turbines, tweak the lines of the hull a little and add a small cannon under it.  Step three. You need to highlight the borders with a thicker line with a pencil, add a lot of details to the wing, circle them, and also add the number 09 for the look.
Step three. You need to highlight the borders with a thicker line with a pencil, add a lot of details to the wing, circle them, and also add the number 09 for the look.  Step four. Lightly shade the entire area of the ship horizontally with light movements, and completely shade the windows, turbine outlets and cannon.
Step four. Lightly shade the entire area of the ship horizontally with light movements, and completely shade the windows, turbine outlets and cannon. 
How to draw the moon with a pencil step by step
Step one. We denote the location of the moon on paper with a square.  Step two. Let's draw a circle, preferably even. Although the surface of the moon is not flat, it will look different from a distance.
Step two. Let's draw a circle, preferably even. Although the surface of the moon is not flat, it will look different from a distance.  Step three. Let's add craters, mountains and hollows on the surface.
Step three. Let's add craters, mountains and hollows on the surface.  Step four. Let's add hatching.
Step four. Let's add hatching. 









