The human nervous system is like a network of wires, through which commands come from the brain and communicate with every part of the body. The brain is a kind of center of such a system. Commands from the brain through nerve fibers come out, which is why laughter arises, appetite is stimulated, sexual desire arises, etc. Nerves serve the brain like messengers. Through special areas nervous system The brain receives information about everything that happens to the body.
Nervous diseases.
The human nervous system is like a network of wires, through which commands come from the brain and communicate with every part of the body. The brain is a kind of center of such a system. Commands from the brain through nerve fibers come out, which is why laughter arises, appetite is stimulated, sexual desire arises, etc. Nerves serve the brain like messengers. Through special parts of the nervous system, the brain receives information about everything that happens to the body. The spinal cord is the main communication route between the brain (Fig. 1) and the entire body (Fig. 2).
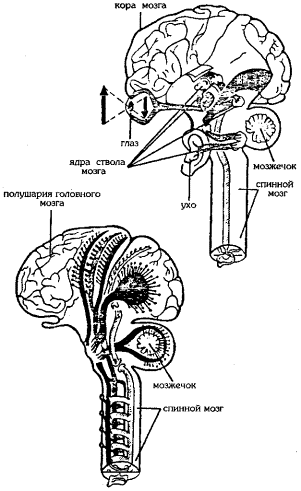
Rice. 1. The structure of the brain
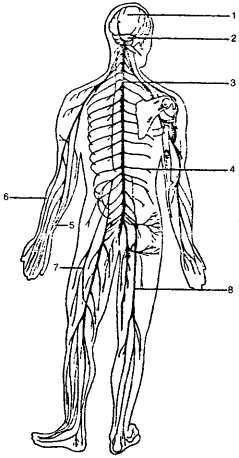
Rice. 2. Human nervous system: 1 - brain; 2 - cerebellum; 3 - spinal cord; 4 - intercostal nerves; 5 - ulnar nerve; 6 - radial nerve; 7 - femoral nerve; 8 - sciatic nerve
central nervous system(spinal cord and brain) is supreme body coordinating the activity of all body systems. The spinal cord is located in the spinal canal, and the brain - in the cranial cavity. The substance of the brain is surrounded by the meninges. The vast majority is located in the brain nerve cells. The bodies of neurons make up the gray matter of the brain (nuclei, cortex big brain and cerebellum). The processes of neurons make up pathways (white matter of the brain). The spinal cord combines nerve trunks in the same way that a telephone cable combines wires. Each trunk has two pairs of nerve roots: anterior - the so-called motor, and posterior - sensitive. Sensory roots transmit signals from the skin, muscles, internal organs to the spinal cord, and from there to the brain. Motor roots transmit signals from spinal cord to different parts of the body. The sensory roots control sensations, and the motor roots control actions. When someone touches us, we feel it through sensory nerve roots (called tactile sensitivity). If we move, impulses from the brain are transmitted through the motor roots. The central nervous system is responsible for all our conscious actions and for responses to external stimuli. Without it, we would not be able to think, move and feel.
But the body can also perform subconscious actions. Some vital organs (for example, the heart, digestive organs) are active, although consciousness does not take part in this. These and many other unconscious actions that are performed automatically are regulated by another nervous system. They call her peripheral nervous system. This part of the nervous system consists of nerves and ganglia. Includes somatic and autonomic (sympathetic and parasympathetic) divisions. The somatic nervous system includes the cranial and spinal nerves (with sensory ganglia), the autonomic nervous system includes the border sympathetic trunk, its branches and autonomic ganglia lying in the walls of the internal organs and near them. The somatic part of the nervous system provides information to the central nervous system and controls the striated muscles of the skeleton and some internal organs (tongue, pharynx, larynx). The vegetative part provides the innervation of the glands and smooth muscles of all other internal organs.
AMYOTROPHIC LATERAL SCLEROSIS- an organic disease of the brain and spinal cord, which is based on an isolated lesion motor neurons(nerve cells and their axons) innervating the muscles of the limbs, tongue, pharynx and larynx. It begins more often at the age of 40-50 years. Characterized by flaccid atrophic paresis and paralysis of the hands, combined with an increase in tendon reflexes, spastic paresis of the legs, speech disorders (dysarthria), and swallowing disorders. The course of the disease is progressive, the disease ends lethally in 2-5 years. The causes of the disease are unknown.
Since there is no specific treatment, prozerin, oxazil (kalimin), vitamins E, B 1 and B 12 are prescribed in courses. Interferon and interferonogens are used. Physiotherapy, massage, therapeutic exercises are widely used. With the development of widespread atrophy, retabolil, nerobol are prescribed.
Apraxia- inability to perform complex purposeful actions (the patient forgot how to dress, fasten buttons, make the bed). It is observed with focal lesions of the brain, with injuries, disorders of cerebral circulation.
ARACHNOIDITIS- inflammation of the arachnoid of the brain or spinal cord, in which adhesions occur between the arachnoid and choroid, followed by circulatory disorders, the formation of cystic cavities. It can occur with general infections, otitis media, inflammatory diseases of the paranasal sinuses, brain tumors, traumatic brain injuries.
Symptoms. There are local and diffuse headaches, nausea, sometimes unsharply pronounced meningeal syndrome and subfebrile temperature. With the predominant localization of arachnoiditis at the base of the brain and the involvement of the optic nerves in the process, a decrease in visual acuity and a limitation of the visual field are observed. Arachnoiditis of other localization proceeds with a clinical picture resembling a tumor of the corresponding localization, and correct diagnosis is possible only with X-ray, tomography, and examination of the cerebrospinal fluid.
Treatment. In the acute phase, treatment is carried out in a hospital. Corticosteroids, veroshpiron, vitamins of group B are prescribed. According to indications, neurosurgical treatment is performed (dissection of adhesions).
ATAXIA- violation of coordination of movements due to damage to the vestibular apparatus, cerebellum, etc. It is manifested by a violation of balance when standing (static ataxia) and disorders of coordination of movements (dynamic ataxia).
If ataxia is suspected, ask the patient to stand with arms outstretched and eyes closed, while the legs should be closed, then touch the tip of the nose with your finger or, lying on your back, touch the knee of the opposite leg with your heel. If a person cannot perform these tasks, then you need to see a doctor.
ATHETOSIS- a type of hyperkinesis, characterized by slow involuntary violent movements due to tonic muscle contractions. Athetoid movements can be observed not only in limited muscle groups ah (face, arm, leg), but also cover the entire musculature. Limited athetosis appears with intoxication lesions of the brain (carbon monoxide, manganese, carbon disulfide), and general athetosis is characteristic of some lesions of the subcortical parts of the brain (hepatocerebral dystrophy, etc.). both sides. As a rule, it is the result of perinatal brain damage in children who have undergone fetal asphyxia.
APHASIA- impaired speech in organic brain damage. Aphasia can be motor, sensory, amnestic. With motor aphasia, patients lose the ability to speak, but understand the speech of others. With sensory aphasia, patients lose their understanding of speech, but can pronounce individual words and phrases. With amnestic aphasia, patients know the purpose of objects, but cannot correctly name them.
INSOMNIA- a very common ailment, characterized by difficulties associated with falling asleep or the process of sleep itself, lasting at least 3 weeks. There are three main types of insomnia: disruption of the process of falling asleep, awakening at night, and early awakening.
1. "I go to bed and can't fall asleep for a very long time"
This condition may be facilitated by:
Stress. Emotional stress includes anxiety, depression, self-pity, anger, and guilt. Its reasons are varied.
Unresolved issues, violation peace of mind, various physical disorders, neurological problems.
Problems of digestion and nutrition. Eating stimulating food and drinks before bed (strong tea, coffee), too plentiful and high-calorie dinner.
Wrong sleep pattern. Daytime drowsiness (afternoon, in the evening) and therefore less need for sleep at night.
Big life changes that can be both good and bad, such as moving to a new place of residence, divorce, death of loved ones, changing jobs, etc.
Failure of the biological clock night work and changing time zones).
External stimuli such as noise.
2. "I often wake up in the middle of the night and lie down, can't sleep"
The causes of interrupted nighttime sleep can be all of the above, plus:
Irritation and anger.
Strong alcohol intoxication, or, conversely, abstinence from alcohol and drugs - on the advice of a doctor or for another reason.
Nightmares, fear of having a nightmare.
Sedentary lifestyle, lack of fatigue during the day.
3. "I wake up very early and can't get back to sleep"
Severe depression.
Alcoholism.
Addiction to sleeping pills.
Treatment. It is necessary to understand the causes of insomnia and try to eliminate them. In the evenings, in order to avoid sleepless nights, try to adhere to the following rules.
Never engage in issues that are bothering you before bed or in bed. To solve them, it is better to choose daytime hours or the beginning of the evening. Eliminate stimulating drinks (tea, coffee, alcohol) in the evenings. Dinner should be light, but exclude raw vegetables and fruits, black bread from it, as they make your stomach growl, which also prevents you from falling asleep. Avoid in the evening any exciting activity (energetic exercise, work, quarrels, etc.). Spend last hour in preparation for sleep, including relaxing exercises and a warm (not hot!) bath with coniferous extract. You can drink an infusion of mint or motherwort. Create a cozy atmosphere in your bedroom, conducive to relaxation. Read Pushkin at night (the rhythm of versification coincides with the natural rhythms of the heart and brain, which calms the overexcited mind). Try to get rid of the noise that can disturb your sleep. It is often easier to fall asleep if a small light is on in the room.
Even if you are a very busy person and are used to doing something all the time or in a hurry somewhere, try to do nothing in the evening and give yourself time and space to think, dream or just take a walk. Maybe this is just what you need to fall asleep peacefully. If you can't get enough sleep on your own, you should see a doctor. Without consulting a doctor, you should not start using sleeping pills, because they become quickly addictive and it becomes much more difficult to fight insomnia.
BULBAR PARALYSIS- a symptom complex consisting of a disorder of swallowing and speech. Occurs when injured medulla oblongata and the nuclei of the cranial nerves, pathways and reticular formation located there. Swallowing disorder, choking and coughing while eating, respiratory disorders are observed. Speech with a nasal tinge, pronunciation of words is disturbed, hiccups, vomiting, disorders of cardiovascular activity, arrhythmias are possible. With the development of bulbar syndrome, urgent hospitalization in a neurological hospital is necessary.
VEGETATIVE-VASCULAR DYSTONIA - a symptom complex characterized by functional disorders in various parts of the autonomic nervous system. Most often, vegetative-vascular dystonia is observed in neuroses and is manifested by various disorders of the cardiovascular, respiratory and gastrointestinal tract. Cardiovascular disorders - palpitations, increased or decreased blood pressure, pallor, sweating; digestive disorders - lack of appetite, belching with air, difficulty swallowing, nausea, hiccups; respiratory disorders - shortness of breath, tightness in the chest. Characterized by complaints of fatigue, restless sleep, emotional lability. There is a slight and transient increase in blood pressure, tachycardia. The manifestations of vegetative-vascular dystonia are very diverse, they can be similar to all diseases at once. The behavior of patients is often intrusive, a lot of absurd complaints made by them can lead the doctor into bewilderment. Sometimes, with the established diagnosis of vegetative-vascular dystonia, the actual disease remains unrecognized. Therefore, the diagnosis of vegetative-vascular dystonia is a diagnosis of exclusion and is made only after an ECG, EEG, visual field examination, examinations by an ophthalmologist, endocrinologist, psychotherapist, urine and blood tests are performed.
Treatment. A complex of health-improving and hygienic measures is recommended, dosed physical exercise, spa and physiotherapy treatment, autogenic training and other methods of psychotherapeutic influence. Prescribe drugs that normalize nervous processes: valerian, bromine preparations, tranquilizers.
HYDROCEPHALIA (dropsy of the brain)- accumulation of excess amount of cerebrospinal fluid in the cranial cavity. There is congenital and acquired hydrocephalus. Congenital hydrocephalus develops as a result of intrauterine infections, intoxications. In children with congenital hydrocephalus, the cranial sutures are dilated, the fontanel is tense, does not pulsate, there is a delay mental development, strabismus, etc. Acquired hydrocephalus develops after infections, brain injuries. It is characterized by an increase in intracranial pressure and is manifested by headache, vomiting.
Treatment. It is necessary to establish the cause of hydrocephalus and treat the underlying disease. Diuretics, mannitol, glycerin, glucocorticoid hormones are used to reduce intracranial pressure. In some cases, surgical treatment is indicated.
HEADACHE. It is a frequent symptom of various diseases of the nervous system of an organic and functional nature. Headache of varying intensity and localization is observed with lesions of the meninges, with increased intracranial pressure, trigeminal neuralgia, skull trauma, inflammation of the paranasal sinuses, with hypertension, atherosclerosis, eye diseases. Often a headache appears in diseases of internal organs (diseases of the liver, kidneys, anemia, chronic poisoning with industrial poisons). Headache can be associated with overwork, emotional overstrain, etc.
Treatment. It is necessary to establish and treat the disease that causes the headache. In addition, painkillers are prescribed (citramon, finlepsin, analgin, acetylsalicylic acid, etc.).
DIZZINESS- sensation of apparent movement of the body in space or surrounding objects around the body. It is often a symptom of damage to the vestibular apparatus, brain stem, cerebellum, and cerebral cortex. May be accompanied by nystagmus, vomiting, gait disturbance, blanching of the skin. An increase in blood pressure that accompanies dizziness often indicates a vascular disorder. Dizziness as a manifestation of the disease may be due to a disease of the inner ear, when the vestibular apparatus is affected by an inflammatory or tumor process. Such patients usually suffer from inflammation of the inner ear (otitis) for a long time, first they have hearing loss, and then dizziness appears. With a tumor lesion, seizures occur against the background of hearing loss, ringing in the ear, and attacks of dizziness gradually become more frequent and intensify.
Often, dizziness is observed with a sharp turn of the head to the side, with a sharp rise in the morning from bed, tilting the head back (during wallpapering, hanging clothes), with a long tilt of the head to the side or anteriorly (weeding, car repair, long sleep on the train, etc.). These dizzinesses are caused by spasm or clamping of the vertebral artery, which supplies blood to the parts of the brain responsible for balance. Dizziness can occur with high or low blood pressure, poisoning, fluid loss (vomiting, diarrhea) or blood loss (bleeding). Accompanied by dizziness and anemia (lack of erythrocytes in the blood - red blood cells), high fever.
Dizziness can also occur in a completely healthy person if, for example, one spins around its axis for a long time or when looking down from high altitude, or when looking at clouds.
First aid. When dizzy, the patient should be laid on his back so that his head, neck and shoulders lie on the pillow, because in this position the kink of the vertebral arteries is excluded. You should avoid turning your head to the side, you need to open the windows, ventilate the room, put a cold bandage on your forehead, you can slightly moisten it with vinegar. After measuring the pressure and temperature, take measures to normalize them, if the heart rate is more than 100 beats per minute or an irregular heartbeat has appeared, and also if nausea and repeated (more than 3 times) vomiting have joined dizziness, it is necessary to call " ambulance". It is necessary to find out the cause of dizziness and treat the underlying disease.
CHILDREN'S CEREBRAL PALSY - are a group of syndromes of impaired motor function, which are the result of brain damage in the prenatal period, during childbirth or in early period child's life. Most often they occur due to infections, intoxications, birth injuries. Children with cerebral palsy do not develop physically well, they begin to sit, walk, and talk with a delay. The main violations are manifested in the form of paresis, paralysis, hyperkinesis. Psychiatric disorders are rare.
Treatment complex, aimed at restoring movement disorders, speech disorders. They constantly carry out massage, physiotherapy exercises, classes with a speech therapist. Assign drugs that normalize muscle tone (elenium, baclofen, etc.), drugs of metabolic action (cerebrolysin, piracetam, etc.). With age, with persistent treatment, motor defects can decrease, in some cases disappear altogether.
STuttering (logoneurosis)- a disease in which there are no pathological changes on the part of the articulatory (speech-conducting) apparatus (larynx, vocal cords, lungs, lips, teeth, tongue), there is no damage to the part of the brain that controls the act of speech, however, the speech control system works inconsistently with the articulatory apparatus. Stuttering is the result of a spasm in one or more of the organs involved in speech production. The flow of words is suddenly interrupted. There is a pause. Sometimes this happens as a result of the rapid repetition in a row of the sound on which the person originally stopped. There are many degrees of stuttering. This can range from a slight inability to pronounce the final letters or syllables, or a situation where the spasm completely fetters the muscles of the tongue and larynx. Very often, the cause of stuttering is emotional excitement.
A stuttering person is usually most troubled by explosive consonants: "b", "p", "d", "t", "k", solid "g". These consonants are formed as a result of stopping the movement of air and pressure on the lips, followed by an unexpected explosion. air flow and exiting through open lips. Stuttering is often corrected if a person follows the rules of reading and slowly, carefully pronounces each syllable.
As a rule, stuttering occurs at a young age, when speech automatisms are not fully developed. Contribute to the development of stuttering stressful situations that the child encounters in childhood (fright, death of a loved one, beloved animal, divorce of parents, constant scandals, etc.) True stuttering increases with excitement, weakens in a calm environment. People who stutter usually sing well and don't stutter when they sing.
Treatment. Speech therapists and psychotherapists are involved in the treatment of stuttering, since the disease is mainly functional in nature and is not associated with a true lesion of the speech apparatus. The prognosis is usually favorable.
STROKE- acute violation of cerebral circulation, which develops most often as a complication of hypertension and atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels. Distinguish between hemorrhagic (cerebral hemorrhage, hemorrhage in the subarachnoid space) and ischemic strokes.
Hemorrhagic stroke (bleeding into the brain) occurs as a result of rupture of an artery during fluctuations in blood pressure or a change in the functional state of the vessels. The development of a stroke can provoke emotional experiences or physical stress. Characterized by a sudden onset, redness of the face, severe headache, loss of consciousness, repeated vomiting and paralysis of the limbs on one side. On the side of paralysis, the corner of the mouth is lowered, sometimes there is a turn of the head and eyes in the direction of paralysis. Blood pressure up to 180/100 mm Hg. Art. and above, tachycardia, after a few hours the body temperature rises to 37-39 ° C, leukocytosis appears in the blood. With extensive hemorrhages, accompanied by a progressive violation of breathing and cardiac activity, the patient may die.
Treatment. In most cases, patients are hospitalized. First of all, the airways are freed from mucus, vomit. The position of the head should be elevated. To compensate for cardiac activity, the introduction of cardiac glycosides is indicated. In the presence of very high blood pressure, it is necessary to reduce it under constant medical supervision to the numbers familiar to the patient (usually not lower than 150-160/90 mm Hg). Enter intramuscularly lasix dibazol, clonidine, papaverine, no-shpu. Effective in the first hours of the disease intravenous slow administration of aminophylline. In severe cases, glucocorticoid hormones (hydrocortisone, dexamethasone) are used. It is necessary to monitor the activity of the bladder and intestines.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage. It occurs when an aneurysm of the cerebral vessels ruptures, less often - with hypertension and other vascular disorders. Characterized by a sudden sharp headache "a blow to the back of the head", vomiting, epileptiform seizures, motor restlessness. Obscuration of consciousness, a stunned state are observed. There is a meningeal syndrome.
Treatment. The patient needs to be hospitalized. Strict bed rest is required for 4 weeks. During the first 7-10 days, epsilon-aminocaproic acid, a sterile solution of glycerin, is injected intravenously. Showing analgesics (baralgin, analgin). During the first 4 weeks, therapeutic exercises and massage are carried out in bed, then, depending on the condition, the patient is allowed to sit and walk. It is necessary to regulate the activity of the bladder and intestines. In the first 8 weeks, the patient should avoid any physical stress and straining in order to avoid re-hemorrhage. When an aneurysm ruptures, surgical treatment is performed.
Ischemic stroke (brain infarction). It often develops in old age as a result of blockage (thrombus, embolism) or a sharp narrowing of atherosclerotically altered cerebral vessels. Provocative moments are emotional overstrain, fatigue, infectious diseases. The disease develops more often gradually, consciousness is preserved. Headaches, dizziness, general weakness, pallor of the skin, transient numbness in the arm or leg are noted. The malaise grows, for several minutes, an hour, sometimes a day, there is an ever-increasing heaviness in the arm and leg, which then sharply weaken and completely stop moving. If the ischemic process develops at night, then in the morning the patient feels that he cannot get up, his arm and leg do not move. If paralysis has developed in the right limbs, then the patient's speech disappears or is sharply disturbed. With the defeat of the left limbs, speech impairment is usually not observed. For cerebral infarction, visual impairment and swallowing disorders are also characteristic.
Treatment. Intravenous slow administration of a solution of aminofillin with a solution of corglycone and a solution of glucose, intravenous drip infusion of reopoliglyukin is recommended. Dexamethasone is used according to indications. From the 4-5th day of the disease, antiplatelet agents (acetylsalicylic acid or trental) are prescribed. The patient needs to carry out massage and therapeutic exercises, monitor the activity of the bladder and intestines, and prevent bedsores (the patient should be rotated regularly). With a mild course and a satisfactory state of cardiac activity, the patient is allowed to get up and walk from the 5-7th day of the disease.
COMA- an unconscious state due to a violation of the function of the brain stem. It is characterized by a disorder of breathing and cardiac activity, a lack of reactions to various external stimuli, and a lack of active movements. May occur with traumatic brain injury, brain tumors, diabetes, strokes, uremia, intoxication with alcohol, drugs. With a mild degree of coma, patients respond to pain stimuli, pupillary and corneal reflexes are preserved. In deep coma, areflexia, atony, mydriasis, gross violations respiration and circulation. In the terminal stage of coma, the vital activity of the patient is preserved only due to artificial ventilation of the lungs and stimulation of the heart. A patient in a coma must be urgently hospitalized.
LUMBAGO (lumbago)- pain that sharply occurs in the lumbar region at the time of physical exertion ( flick, lifting weights).
Symptoms. The disease develops acutely: at the moment of tension, severe pain in the lower back suddenly appears, the patient cannot bend and unbend, freezes in one position, sometimes falls from pain. The pain increases sharply with any movement, coughing, sneezing. Palpation reveals tension in the back muscles. After a few days, the pain disappears, the range of motion in the spine is gradually restored.
Treatment. Assign bed rest, analgesics (analgin, baralgin, finlepsin). Rubbing with Voltaren ointment, menovazine, mustard plasters are shown.
MENINGEAL SYNDROME. The syndrome of irritation of the meninges can be observed with intoxication, general infections, increased intracranial pressure, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and also with meningitis. Due to irritation of the nerve roots, reflex muscle tension occurs (stiff neck - restriction or inability to bend the head forward, Kernig's symptom - the inability to straighten the leg at the knee joint when the leg is bent at a right angle in the hip joint). Important components meningeal syndrome are headache, sometimes vomiting, hypersensitivity to light, noise, mental disorders are possible.
MENINGITIS- inflammation of the pia mater of the brain and spinal cord. There are primary and secondary meningitis. Primary (epidemic cerebrospinal) meningitis is caused by meningococcus. Secondary meningitis often develops as a complication of common infectious diseases (otitis media, boils, influenza, mumps), caused by various pathogens (coccal flora, viruses, etc.).
Symptoms. The clinical picture of both forms of meningitis is similar. The onset of the disease is acute, the body temperature rises to 39-40 ° C, there is a severe headache, vomiting, agitation, often confusion and delirium. Observed meningeal syndrome(see) various expressiveness. Due to the involvement of the cranial nerves in the process, strabismus, impaired convergence and accommodation may occur, nystagmus, anisocoria are possible. In the blood, neutrophilic leukocytosis, ESR is accelerated. The cerebrospinal fluid is turbid, flows out in a stream, contains many proteins, a large number of neutrophilic leukocytes and meningococci. Complications are possible: infectious-toxic shock, cerebral edema.
Treatment. Patients are hospitalized. Carry out etiotropic, detoxification and dehydration therapy. Assign benzylpenicillin intramuscularly 6-8 times a day in large doses for 7-10 days. In case of intolerance to penicillin or resistance of the pathogen to it, ampicillin, levomycetin, oxacillin, tetracycline, metacycline are prescribed. For detoxification, a 5% glucose solution, isotonic sodium chloride solution, plasma, albumin, etc. are administered intravenously. Lasix, mannitol, etc. are administered to prevent cerebral edema. In severe forms, corticosteroid drugs are indicated. For the treatment of convulsive syndrome, seduxen (diazepam), sodium hydroxybutyrate is used. Patients are discharged from the hospital after receiving negative results of a double bacteriological examination.
MIGRAINE- a disease manifested by attacks of headache, mainly in one half of the head (hemicrania). Young women are more likely to suffer from migraines. The attack is preceded for 10-20 minutes by malaise, irritability, heaviness in the head, drowsiness, flashing "flies" before the eyes. The pain is throbbing, accompanied by redness or blanching of the face, redness of the eyeballs, nausea, and sometimes vomiting. The duration of the attack is from several hours to several days. The disease is not progressive in nature, is not accompanied by signs of organic brain damage, with age the attacks become less intense.
Treatment. Since there is no consensus about the true nature of the disease, symptomatic agents are used. Some patients are helped by heat (warmers to the feet, mustard plasters), others by cold, others by tight pulling of the head with a towel, etc. During an attack, the patient needs absolute rest. Of the medicines, sedatives (valerian, bromine preparations), tranquilizers (meprotan, elenium), antispasmodic and vasodilators (dibazole, papaverine), analgesics (phenacetin, amidopyrine, nomigrofen) are prescribed. Reduce attacks difenin, phenobarbital, anaprilin. General recreational activities are recommended (stay on fresh air, sufficient sleep, work and rest schedule, sports).
MYELITIS- Inflammatory disease of the spinal cord. It can occur as a complication of common infectious diseases, traumatic injuries of the spine or spinal cord. Focal myelitis is characterized by an acute onset, fever, back pain, chest pain, numbness and weakness in the legs, urinary retention. In severe forms, paralysis of the limbs, sensory disturbances according to the conduction type, and a disorder of pelvic functions occur.
Treatment aimed at the underlying disease, a complication of which was myelitis. In most cases, patients need to be hospitalized. Antibiotics, analgesics, sedatives and anti-inflammatory drugs, vitamins are used. If necessary, surgical treatment is carried out.
NEURALGIA- defeat of peripheral nerves most often due to cooling, infection, intoxication, trauma, metabolic disorders. Neuralgia is characterized by paroxysmal pains of a cutting, shooting nature with extensive irradiation, corresponding to the zone of innervation of the sensory nerve.
trigeminal neuralgia more often occurs with various inflammatory diseases of the teeth, jaws, paranasal sinuses. It is characterized by intense bouts of spontaneous pain in the face on one side, lasting from a few seconds to 1-2 minutes. An attack of pain occurs spontaneously and is often accompanied by convulsions of the mimic muscles. The study sometimes reveals soreness of the exit points of the trigeminal nerve, the presence of "trigger" zones, with a light touch to which an attack is provoked.
Neuralgia of the occipital nerve characterized by pain in the back of the head. They are of a knocking, breaking nature, gradually spreading anteriorly along the surface of the head, radiating from the back of the head to the temple and eye. Pain is aggravated by turning the head, by probing the neck, sneezing and coughing, often causing nausea and vomiting.
Neuralgia intercostal accompanied by pain along the intercostal space, usually one, but 2 and 3 intercostal spaces may be affected. The pains are constant, aching. They are aggravated by walking, breathing, turning the body, palpation of the ribs and intercostal spaces.
Treatment depends on the nature of neuralgia and is carried out under the supervision of a physician. Prescribe anticonvulsants, sedatives (seduxen, trioxazine), vitamin B 1 , B 12 , nicotinic acid, physiotherapy (UHF, diadynamic currents, electrophoresis with novocaine). Acupuncture has a good effect. With the ineffectiveness of conservative therapy, surgical treatment is indicated.
NEURITIS- inflammation of the nerve. (Neuritis is an obsolete name; it is now customary to use the term "neuropathy" since most peripheral nerve lesions are non-inflammatory in nature.) In clinical practice, neuropathies of the facial, radial and tibial nerves are most common.
Neuropathy of the facial nerve- most often has a vascular nature. It occurs after hypothermia, the peak incidence occurs in September and March, that is, when the winds begin in the off-season, and people go without hats and scarves, in light raincoats, often fall into drafts. The facial nerve emerges from the cranial cavity in the behind the ear region. With hypothermia of the head, a spasm of the vessels that feed the nerve occurs. Deterioration of nutrition leads to swelling and jamming of the nerve in the walls of the bone canal, which further worsens the nutrition of the nerve. The patient, getting up in the morning, notes a slight aching pain behind the ear, when trying to brush his teeth, he notices that water flows out of the corner of his mouth, having breakfast, he notes that food constantly gets between his cheek and teeth, making it difficult to chew food. Approaching the mirror, he sees that his face is immobilized on one side, and his mouth is drawn to the opposite (healthy) side. The eye on the diseased side does not close, the forehead does not wrinkle, when trying to smile, the corner of the mouth is motionless. Sensitivity on the face (when pricked with a needle) is preserved.
A similar picture can be caused by diseases such as inflammation of the inner ear, tumor of the auditory nerve, multiple sclerosis, brain tumor, stroke in the brain stem, diabetes mellitus.
Neuropathy of the radial nerve. Complaints about the inability to unbend the fingers of the hand and raise the hand up are typical, while the hand is compressed into a fist well. The patient cannot pat with his hand on the table, cannot tap on it with his fingers. Usually these disorders occur after the use a large number alcohol the night before and an uncomfortable night's sleep. For example, if the patient sleeps without a pillow, with his arm under him, or the spouse sleeps on his shoulder at night.
Neuropathy of the small tibial nerve. Complaints about the inability to stand on the heels, the inability to put on slippers on their own, the foot seems to "hanging". When walking, the patient stumbles on level ground, the gait is also unusual: a person tries to lift or throw his leg forward and up so that the foot does not cling to the floor. Such a disorder often occurs after severe sciatica, hypothermia of the legs, an allergic reaction (bee sting), poisoning with chemicals (alcohol, insecticides), atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower extremities, diabetes mellitus, prolonged forced sitting, especially cross-legged.
Treatment. The sooner the patient sees a doctor, the greater the chance of success. If you do not take action in the first 3-4 days of the disease with neuropathy of the facial nerve, then the face will remain motionless forever. Apply dry heat, aspirin, nicotinic acid, chimes, hormones, adhesive traction, electrical stimulation, acupuncture. If neuropathy of the facial nerve is a manifestation of another disease, the cause is treated first, but at the same time all measures are taken to restore the nerve, so as not to waste time.
With neuropathy of the radial and small tibial nerve, a similar treatment is used.
FAINTING- a short-term drop in vascular tone, accompanied by anemia of the brain. Manifested by sudden weakness, dizziness, loss of consciousness (for a few seconds or minutes). It is observed in some cardiovascular diseases, blood loss, acute pain, severe excitement, etc.
First aid. First of all, it is necessary to determine whether consciousness has been lost, for this patient they call loudly by name, slap on the cheeks, determine the width of the pupils, whether they react to light. This information will also be necessary for the doctor of the clinic or ambulance. The patient is laid with raised legs, freed from tight clothing, sprayed on the face cold water, give a sniff of cotton wool moistened with ammonia, cologne. A simple syncope does not require treatment, however, during it, the patient may vomit, and if he falls, he may break his dentures. Fragments of prostheses, food can get into the trachea, bronchi, which threatens death from suffocation. The patient must be turned on his side, the prostheses should be removed from the mouth, the vomit should be removed, and a cotton swab moistened with ammonia should be smelled. If consciousness is not restored after 5-7 minutes, and even more so if the patient hit his head, urgent hospitalization is necessary.
BRAIN TUMORS - can be primary (from the membranes, brain substance) and secondary (metastatic). General cerebral symptoms are characteristic: headache, nausea, vomiting, bradycardia, epileptic seizures, mental disorders, constant fatigue. Symptoms of a focal lesion depend on the location of the tumor and can be manifested by paresis, paralysis, speech disorders, visual impairment, impaired coordination of movements, etc.
If a brain tumor is suspected, an urgent inpatient examination of the patient is necessary to make an accurate diagnosis.
TUMORS OF THE SPINAL CORD - There are primary (developing from the structures of the spinal cord) and secondary (metastatic). Tumors of the prostate, kidneys, stomach, thyroid gland, etc. metastasize to the spinal cord. Symptoms of spinal cord tumors are determined by the location of the tumor; paresis, paralysis, disturbances in pain, tactile and temperature sensitivity, pelvic disorders, etc. can be observed.
If a tumor of the spinal cord is suspected, the patient should be sent to a hospital for examination (studies of the composition of the cerebrospinal fluid, myelography, etc.)
OSTEOCHONDROSIS- cm. Radiculopathy discogenic.
SHELLING PARALYSIS (Parkinson's disease)- occurs more often in old age, after 50 years. Parkinson's disease is based on a hereditary defect in dopamine-synthesizing brain cells. The same defect can manifest itself after craniocerebral trauma, taking large doses of antipsychotics, carbon monoxide poisoning, etc. Rhythmic trembling of the limbs is characteristic, gradually increasing and spreading to the lower jaw, tongue, and head. Trembling is expressed at rest, decreases with movement, disappears during sleep. The patient becomes inactive, with a characteristic flexion posture of the body, walks in small steps, his face is mask-like, his speech is monotonous, quiet. The course of the disease is progressive. In the late stage - immobility, cachexia.
Treatment. Assign cyclodol (parkopan, artan). In the developed stage, levodopa, nakom, madopar, etc. are used.
RADICULOPATHY DISCOGENIC ("banal radiculitis")- diseases caused by damage to the roots of the spinal cord due to osteochondrosis of the spine. Osteochondrosis of the spine is a degenerative-dystrophic process in which the intervertebral discs lose their shock-absorbing function and significant changes occur in the fibrous ring of the disc, the ligamentous apparatus of the spine and the structure of the vertebral body. In the segment of the affected disc, relative instability of the spine occurs with the development of osteophytes of the vertebral bodies (spondylosis), damage to the ligaments and arthropathy of the intervertebral joints (spondylarthrosis), protrusion of the disc (protrusion or hernia), while osteophytes can compress the nerve roots, causing severe pain(Fig. 3). The immediate cause of pain is often weight lifting, awkward movement, infections, etc. The shape of the spinal column is such that the maximum load falls on the lower cervical, lower thoracic and lower lumbar regions, therefore, the clinical picture most often shows signs of root compression at these levels.
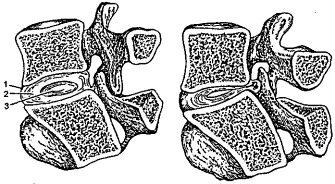
Rice. 3. Left - normal position in the intervertebral disc; on the right - extrusion and infringement of the pulpous nucleus: 1 - intervertebral disc; 2 - fibrous ring of the disc; 3 - nucleus pulposus.
Symptoms. Characterized by pain and stiffness in the corresponding part of the spine, fatigue of the back muscles. With cervical sciatica - pain in the neck, radiating to the arms and neck, forced position of the head, straightening of the cervical lordosis. The pains are aggravated by coughing, sneezing, moving the head. Usually, the pain is most pronounced in the upper parts of the arm, and there are paresthesias in the hands. With thoracic radiculitis - pain surrounding the chest and abdomen. With sciatica - pain in the sacrum, accompanied by tension of the long back muscles, general stiffness. Pain is often accompanied by weakness of the flexors and extensors thumb leg or whole foot. The Achilles reflex is often absent. The defeat of the L4-root proceeds with a picture of the defeat of the femoral nerve: pain along the anterior surface of the thigh and in the knee joint, sometimes weakness of the quadriceps femoris muscle and loss of the knee reflex. Tension of the lumbar muscles, smoothing of the lumbar lordosis are observed. Complete prolapse of a herniated disc leads to compression of the ponytail and paralysis of the legs, feet, saddle anesthesia, dysfunction of the pelvic organs.
The blood picture is usually normal. Significant narrowing of the intervertebral space, sclerosis, osteophytes, etc. are determined radiographically.
At the first unexpected attack, it is recommended to immediately call an ambulance or a local doctor, since an ectopic pregnancy, renal colic, intestinal obstruction and other diseases can be hidden under the guise of sciatica. To make the correct diagnosis, consultation with an experienced specialist is necessary.
Treatment. During periods of exacerbations, bed rest is recommended (it is necessary to lie on a hard surface to unload the spine), physiotherapy, massage, stretching of the spine to decompress the roots, analgesics (baralgin, indomethacin, analgin, acetylsalicylic acid), novocaine blockade, B vitamins, seduxen, elenium, sibazon, etc. When inflammation subsides, physiotherapeutic procedures are indicated - diadynamic currents, ultrasound, electrophoresis with novocaine. With prolonged severe pain that is not amenable to conservative therapy, surgical treatment is indicated.
MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS- a disease of the nervous system, characterized by the appearance in the brain and spinal cord of foci of demyelination, which eventually either disappear or are replaced by glial scars. The etiology is not fully understood, the cause of the disease is considered to be a virus that causes an autoimmune reaction with the destruction of the myelin sheath of nerve trunks and conductors. Persons at the age of 18-50 years are ill. Often the disease occurs in women after childbirth.
Symptoms. The disease often begins with visual disturbances, in which vision in one or both eyes deteriorates sharply, double vision occurs. These symptoms go away after a few days or after 2-3 weeks. Later, there is a period of complete clinical recovery, which can last from several hours to several years. During the disease, unsteadiness when walking, dizziness, weakness in the legs develop. Bladder function is often impaired. Over time, remissions become shorter and longer, and relapses become longer, and after a few years, patients acquire a disability of one group or another. Euphoria is noted, and in advanced stages dementia is often observed.
Treatment. At the first attacks of the disease, nonspecific desensitizing therapy is carried out: diphenhydramine (suprastin, tavegil) inside, ascorbic acid, vitamin B 1 injections, prozerin inside, diathermy of the adrenal region. With exacerbations of the disease and the development of severe ataxia or weakness in the legs, hormonal and symptomatic therapy is carried out in the hospital.
Syringomyelia- congenital chronic disease of the spinal cord with the growth of gliosis cells in its gray matter.
Symptoms. A characteristic feature is a disorder of temperature and pain sensitivity while maintaining tactile (tactile) sensitivity. With damage to the cervicothoracic spinal cord, pain sensitivity drops out on the arms, shoulder girdle, upper section chest and back. Characterized by atrophy and weakness of the muscles of the hands, especially the hands, there are often scars from burns that patients inflict on themselves due to loss of sensitivity. When the glial tissue dies and cavities form in the gray matter, spastic paresis in the legs may join. The course of the disease is long (several decades).
Treatment symptomatic, conduct courses. The course of treatment includes injections of ATP intramuscularly, injections of prozerin, vitamin B 1 , B 12 . Massage of the affected muscles, hydrotherapy, ionization with potassium iodide are recommended. In severe cases, surgical treatment is performed.
SEVERAL STATES. Convulsive conditions are characterized by involuntary contractions of individual muscle groups or muscles of the whole body. Generalized convulsions are observed in various diseases of the brain (epilepsy, trauma, tumors, encephalitis, meningitis, vascular disorders), in eclampsia of pregnant women. Often convulsions occur with general infections and intoxications, especially in children. Local cramps are observed with overexertion individual groups muscles due to the performance of frequently repetitive fast movements (musicians, athletes, etc.).
In children (often infants and early childhood) against the background of an increase in temperature, clonic and clonic-tonic convulsions in the muscles of the trunk and extremities can be observed. If convulsions recur with each febrile state, then it is advisable to prevent their development by prescribing phenobarbital at the beginning of an infectious disease in doses corresponding to the age and weight of the child.
BRAIN INJURIES. According to the degree and nature of brain damage at the time of injury, there are: concussion with the presence of only cerebral symptoms; contusion (bruise) of the brain with the presence of cerebral and focal symptoms; severe traumatic brain injury, accompanied by prolonged loss of consciousness with life-threatening symptoms of damage to the trunk and subcortical formations, often combined with compression of the brain by intracranial hematomas.
Concussion. With a mild degree of concussion, a short-term loss of consciousness (several seconds or minutes), headache, nausea, and vomiting are observed. A moderate concussion is accompanied by a short-term or relatively long-term loss of consciousness (up to several tens of minutes), after which nausea, vomiting, headache, dizziness, spontaneous nystagmus, retrograde amnesia, cardiovascular disorders, vegetative disorders are observed.
For injury (concussion) the brain is characterized by the same symptoms as with a concussion, but with more pronounced and persistent focal symptoms. In accordance with the location of the lesions in the brain, sensory disturbances, paresis, more persistent and severe mental disorders are observed. Brain contusion is usually combined with intracranial hemorrhages. In the late period, residual effects of focal brain damage, the development of epileptic seizures are often observed.
At severe traumatic brain injury there is a long-term impairment of consciousness, reaching the degree of coma, in combination with severe respiratory disorders, cardiovascular activity, metabolic processes and thermoregulation. Fractures of the base of the skull due to the simultaneous violation of the integrity of the membranes and rupture of blood vessels usually occur with bleeding from the ears and nose, hemorrhages in the conjunctiva and bruising around the orbit.
The source of hemorrhages that occur during brain contusions are either the arteries of the pia mater (subarachnoid hemorrhages) and the brain itself, or the venous sinuses (subdural hemorrhages) and the vessels of the dura mater (epidural hemorrhages). With hemorrhages, hematomas are formed, causing compression of the brain. Epidural and subdural hematomas are characterized by an increase in cerebral and focal symptoms after a "light" period after injury. With a rapidly growing hematoma, there may not be a "light" gap. An important diagnostic sign is a wide pupil on the side of the hematoma, as well as the development of local convulsive seizures and paresis on the side opposite to the localization of the hematoma.
Treatment. Patients with brain injuries must be urgently hospitalized. In mild forms of concussion, bed rest and complete rest for 5-7 days are indicated. If there is a headache, dizziness, asthenic syndrome, tranquilizers, analgesics, and in some cases diuretics are prescribed. During the first 5 days, even with a mild concussion, it is necessary to constantly monitor the patient's condition so as not to miss the first symptoms of a developing hematoma. In more severe forms of concussion and bruising in the acute period, rest, bed rest, cold on the head are prescribed, and when excited, tranquilizers are prescribed. To combat cerebral edema, diuretics are used: lasix (furosemide). A good effect is obtained when glycerin is administered orally in apple or other acidic juice in a ratio of 1:3 (1 dose of glycerin and 3 doses of juice) - take 1 tablespoon 4-5 times a day for 7-10 days. To reduce intracranial pressure under strict medical supervision, you can use glucocorticoids - hydrocortisone, dexamethasone. Prescribe drugs that regulate cardiovascular activity. If epi- and subdural hemorrhage is suspected, special studies (echoencephalography, angiography, etc.) and surgical treatment are carried out.
CHOREA- hyperkinesis, characterized by scattered erratic twitches of the muscles of the face, trunk and limbs. Patients are fussy, restless, constantly grimacing. Twitching interrupts voluntary movements, as a result of which the latter acquire the character of uncoordinated ones. Typical dancing gait.
Chorea most often occurs in children as a result of rheumatic brain damage. The most characteristic clinical manifestations are involuntary uncoordinated movements against the background of a decrease in muscle tone, emotional lability, aggressiveness, tearfulness.
Forecast favorable. With proper treatment, most patients recover completely.
Chorea of Hettington- a hereditary disease that manifests itself at the age of 30-40 years. Mental disorders develop, memory impairment, involuntary movements in the arms, legs, facial muscles, tongue. Later, progressive dementia joins, reaching the complete disintegration of the personality.
Treatment. To mitigate hyperkinesis and impulsivity, haloperidol is prescribed 1 tablet 3-4 times a day, chlorpromazine, piracetam (nootropil) 2 capsules 2 times a day.
Forecast adverse. All patients die in the stage of severe mental degradation.
CHRONIC VASCULAR INSUFFICIENCY OF THE BRAIN. Usually the disease develops with atherosclerosis of the cerebral vessels in the elderly. Chronic vascular insufficiency can develop against the background of normal pressure (dyscirculatory encephalopathy) and against the background of hypertension (hypertensive encephalopathy). The slow development of insufficiency of cerebral blood supply leads to metabolic disorders in brain cells. Against this background, there is a decrease in efficiency, memory impairment, sleep disturbances, headaches and dizziness appear.
Treatment. Piracetam (nootropil), trental are used to improve cerebral circulation. In hypertension, appropriate treatment is necessary. You should observe the regime of work and rest, eat dairy and vegetable food, stop drinking alcohol and smoking.
epiduritis- purulent inflammation of the epidural tissue of the spinal cord. Most often, it develops when an infection enters the epidural space from purulent foci (abscesses, boils, etc.) or with septicopyemia. With the restriction of the purulent process, an epidural abscess is formed, with a diffuse process - phlegmon.
Symptoms. The disease develops acutely, the temperature rises to 39-40 ° C, a severe general condition is characteristic, patients complain of severe pain in the spine, and after a while, symptoms of spinal cord compression (paresis, paralysis, disorders of pain, tactile and temperature sensitivity and pelvic disorders).
Knowing the individual pros and cons of your type will make it much easier for you to choose a job search strategy. All aspects of this process are the study of existing vacancies, the search for potential employers, contacts with them, the preparation of documents (CVs, etc.), agreements on...
Most often nervous system damage people are the result of infectious diseases. Diseases of this kind, in addition to the occurrence of complications dangerous to human health, contribute to the development of damaging factors of the nervous system.
For example, a patient with influenza may develop a hypertensive (hypotonic) crisis. On the face, there are obvious violations of the body's activity, both in the nervous and emotional terms. More than others, people with injuries in the region of the skull, who received a concussion, who regularly take alcoholic beverages, are susceptible to this.
Disease classification
Influenza is capable of “giving out” a serious complication that will result in a severe lesion of the nervous system. The list is very extensive, the favorites are as follows:
1. Meningitis- the inflammatory process affects the soft shell of the brain.
2. Encephalitis - brain tissue is inflamed.
3. Inflammatory processes affecting the arachnoid membrane of the brain are called arachnoiditis.
4., sinusitis, can also be safely included in this list.
As a result, such a chain of inflammatory processes can lead to swelling of the brain tissue.
Symptoms of arachnoiditis, principles of treatment
The disease arachnoiditis becomes noticeable, approximately on the seventh day, after a person has fallen ill with the flu.
Inwardly, the patient feels an improvement in his health, but in fact, a more dangerous disease is hiding here. Arachnoiditis reaches its true strength, the peak of its capabilities, a few months after the end of the infectious disease (flu).
The disease has its own classification, depending on the area of manifestation of the lesion. It is characterized by the presence of acute pain in the head, mainly in the frontal part, bridge of the nose. Simultaneously with this, vomiting reflexes are continuously repeated. During normal walking, the patient sways noticeably from side to side. Hearing loss occurs - ear canals are blocked. During an exacerbation, there is a possibility of seizures with convulsions.
A common feature for all types is the presence of a severe headache, which does not represent the body, not the slightest opportunity to rest. On the contrary, it periodically increases as a result of increased physical, mental stress, the upcoming cooling or overheating of the body above acceptable standards. During severe pain, the onset of gag reflexes is possible.
The extreme danger of the disease lies in the fact that the cerebrospinal fluid ceases to circulate normally, which leads to inflammatory processes in the area of the arachnoid. In the acute stage, doctors use antibiotics for therapy. For the chronic form of the disease, absorbable substances are prescribed, such as agave juice (aloe), vitamins that produce a general strengthening effect (group B). During the onset of seizures, special drugs are used against convulsive muscle contraction.
If all treatments are carried out on time, then the chances of strengthening those reeling from arachnoiditis increase significantly. Diagnosis of the disease at an early stage, qualified therapy of infectious diseases are the main preventive actions necessary for such a situation.
Signals from meningitis
In the case when the nasopharynx is the site of the formation of intense inflammatory processes, then there are often situations of disruption of the normal functioning of the meninges. This fact, indicates the approach of another dangerous type of influenza - meningitis.
For infection, the preferred method of transmission is airborne, by means of mucus, saliva, coughing, normal conversation. For some, an infectious disease manifests itself in the form of a runny nose, while no significant deviation in their health is observed, there is no obvious need to seek medical attention. medical care. It follows from this that often, healthy on appearance people are carriers of infectious diseases.
Of particular danger are children, people who have a reduced body resistance to various diseases, that is, those with low immunity. The chances of being infected with meningitis viruses increase with the use of low-quality food, water. In order to significantly reduce the likelihood of infection, it is necessary to thoroughly boil the water before using it.
At the same time, it is necessary to pay due attention to strengthening your immunity: adhere to key principles, take vitamins, and systematically engage in recreational physical education.
Regular walks in the open air, combined with breathing exercises, if possible, will be appropriate.
Symptoms of the starting days of the disease are characterized only by the appearance of fever, pain in the head region. After a certain period of time, they begin, there is weakness, fatigue, the feeling of appetite is lost.
To these symptoms, a runny nose, a sensation of sore throat are gradually added. Over time, the effect of all symptoms intensifies. The patient often has nausea, vomiting, which do not bring relief. The feeling of irritation to all external factors increases, inhibition occurs, and insomnia is observed.
Further, events can develop more negatively: vomiting increases, there is confusion in the mind, delirium, convulsions occur. Reddish, purple smudges appear all over the body. The most “popular” place of their manifestation is the muscles of the buttocks, thighs, legs. Much more rarely, the face area joins this list. The danger of ill health from independent, unskilled treatment for meningitis becomes doubly relevant. The timeliness of the start of therapy is extremely important, because in this situation the clock is counting. If the moment is missed, and meningitis is already “lighting its stars” with might and main, then delay is unacceptable - an emergency call to an ambulance is the only right decision.
The most characteristic symptom of meningitis is considered sharp, when you try to bend your head forward to your chest. Two main types are classified: serous, purulent. In the first, in most cases, everything is limited to a slight inflammation of the brain. Of course, this statement is relative, since we are talking about the most important organ of the human body. Speaking about purulent inflammation, the situation looks much more threatening, since the meninges are the place of accumulation of purulent masses. This circumstance is extremely dangerous, requires immediate treatment. The presence of a purulent form of meningitis is determined by the appearance of a rash on various parts of the body.
After determining the diagnosis, an intensive treatment of the disease is carried out, with the use of drugs from the class of antibiotics. The use of drugs in this group provides patients with not only survival (a significant reduction in deaths), but gives them the opportunity to hope for a full life after the rehabilitation period.
Recurrence of meningitis is extremely rare. Reliable protection is provided by regular vaccinations. They are made for adults, children from 2 years old. The use of vaccines maintains immunity at the proper level for several years. Further, vaccinations must be repeated.
In the case of a viral form of the disease, antibiotics are practically not used, but special antiviral drugs are used. On this moment, we can confidently state the following fact that with the timely detection of the disease, the correctly chosen course of therapy, no negative consequences will not appear. Those who have had a meningitis disease, after discharge from the hospital, systematic control examinations by a polyclinic doctor are recommended: for the first three months every thirty days, and then once a quarter for a year. Finally, in the future, the regularity of inspections should be at least once every six months.
It is urgently required to completely exclude the use of alcoholic beverages, to overcome addiction to tobacco. If possible, it is shown to undergo therapeutic courses that stabilize human health, in the respective sanatoriums.
Neuritis - how to save nerves
Another type of disturbance of the activity of the nervous system is called "polyneuritis", which is also a consequence, especially carried on the legs. Usually, the onset of this disease is accompanied by the onset of general weakness in the upper and lower extremities, a slight increase in temperature, and the appearance of aching fingers. The weakening of the limbs can progress, up to mild paralysis. This condition can be aggravated by a violation of swallowing, speech functions.
Most often, after suffering influenza the nerves of the face, elbows, as well as the radial, sciatic nerves are affected. When a diagnosis is made, an increased protein content is observed in the cerebrospinal fluid. The disease can last up to three months, but with timely treatment, body functions will certainly be restored.
A more negative version of events develops when the lesion affects the vagus nerve. The threat to human life increases dramatically, as the process of breathing is seriously disturbed.
Damage to the nerves of the face is a frequent complication after infectious diseases. Mimic facial muscles suffer, which is expressed by a distorted mouth, the ability to raise eyebrows exclusively on the healthy side of the face.
Problems with the ulnar nerve exclude the possibility of flexion movements in the metacarpophalangeal joints. The position of the hand is motionless, comparable to the claw of a bird.
In cases of the elderly, the flu often comes with a complication of hearing loss when the nervous system affects the auditory nerve. A person has an imperceptible, very gradual hearing loss, but after some time even a quiet conversation becomes inaudible. A stable feeling of constant is created. The result of such a complication may be the final hearing loss.
In order to cure acoustic neuritis, recommendations traditional medicine are reduced to the use of heat in dry versions - sand heated to hot, warming compresses, heated salt in a cloth bag. However, I repeat that any manipulations with your health based on home recipes are strongly recommended for use only in consultation with a qualified doctor.
1. Prepare an emulsion of propolis with oil, alcohol. The use of this remedy eliminates tinnitus, restores auditory functions in most cases. The emulsion is prepared as follows:
- Take forty grams of propolis, after grinding it. The resulting mass is placed in glass vessel where one hundred milliliters of alcohol is located. Infuse for a week at room temperature, while shaking the contents every day. Filter, mix the infusion with olive oil in a ratio of 1:4. The mixture must be shaken before each use.
2. Place a wick made of gauze soaked in emulsion in the ear canal for two days. The procedure is carried out with a break of one day, only ten times.
3. Daily use of a few slices of lemon helps to improve the functioning of auditory functions.
4. Combine one teaspoon of birch tar with a glass of warm milk. It is indicated for use three times before meals. The course of therapy is 60 days. This procedure is very helpful in restoring hearing.
5. Wrap fragrant geranium leaves in linen, apply to the place where pain is felt, attach with a bandage, cover with something warm on top.
Now a few words about a possible complication of the body, after an unskilled approach to therapeutic question with an infectious disease. The recommendations below home treatment, perhaps some of you will be given all possible assistance to cope with this ailment by correcting body health.
1. Collect dandelion flowers in a glass container. Fill a jar with stacked flowers with vodka in a ratio of 1 to 3, put for two weeks in a place without lighting. Then filter the infusion, make them rub the sore spots. The above tincture has proven itself quite well as therapeutic agents, in cases such as bruises, sprains, arthritis, bedsores.
2. We take 20 grams of crushed tansy flowers, put them in water that has just been boiled, with a volume of one liter. We wrap the container with a warm cloth, insist for four hours, filter it with gauze. Use the resulting infusion in a warm state, half a glass three times 30 minutes before meals.
3. One hundred grams of thyme are taken, placed in a container with one liter of boiling water, covered with a lid and kept on low heat for five minutes. After that, filter, pour into a pre-prepared bath. The procedure is done one hour before bedtime. The duration of the course is two weeks. Such a bath provides indispensable help for rheumatism of the joints, edema, and sciatica.
To reduce the likelihood nervous system damage efforts should be made to exclude Everyday life stress, the use of alcoholic beverages, pay due attention to the prevention of infectious, non-communicable diseases, healthy lifestyle life.
Neurology (diseases of the nervous system) is a broad field of medicine that studies the issues of diagnosis, origin and treatment of diseases that have arisen on the basis of nerves. It is worth noting that the problems that neurology studies are more often of organic origin - nervous diseases caused by injuries, vascular diseases and hereditary diseases. But nervous and mental illness(neurosis) are already more within the competence of a psychotherapist.
Modern medicine has in its arsenal against nervous diseases many methods for diagnosing diseases: magnetic resonance imaging, polysomnography, electroneuromyography, electroencephalography, and many others. To date, the most common complaints of diseases of the nervous system are: pain in the neck and back, fainting, chronic headache, convulsions, memory impairment, bad dream, memory problems. But it should also be remembered that one of the most important areas of neurology is the prevention of stroke and other diseases of the nervous system.
Nervous diseases are quite dangerous for human life. After all, one should remember this dependence: diseases of the nervous system inevitably lead to a deterioration in the functioning of other organs and systems, and vice versa. It is worth remembering that it is possible to develop a disease on a nervous basis, which at first glance is not at all associated with nervous diseases. Nervous diseases develop gradually (and a person does not attach importance to them at first) or too rapidly.
Infections, injuries, development of tumors, vascular diseases and severe heredity are the main reasons that indicate the risk of developing nervous diseases.
The symptoms are different:
- Motor - paresis, paralysis, trembling of the limbs, impaired coordination;
- Sensitive - prolonged headache (migraine), pain in the spine, back and neck, impaired visual apparatus, hearing, taste;
- Others are epileptic and hysterical seizures, fainting, sleep disturbance, fatigue, speech disturbance, etc.
Nervous diseases - symptoms. The most common diseases
Arachnoiditis - nervous diseases that are characterized by inflammation of the network of blood vessels that cover the human brain - the arachnoid membrane of the brain. The causes of this disease of the nervous system are injuries, intoxication and infection that enters the membrane of the brain. Separate arachnoids
you both anterior and posterior cranial fossa, basal and spinal arachnoiditis. Meningitis is an acute inflammation of the membranes of the brain, which belongs to the category of "nervous diseases". Symptoms are as follows: fever, unbearable pain in the head, nausea and vomiting, which does not bring relief, impaired muscle tone. At the first symptoms max it is necessary to hospitalize the patient! Next, the patient is given a spinal puncture, followed by a determination of the treatment of the disease. Meningitis is a very serious disease and requires urgent treatment.
Migraines are nervous diseases that manifest themselves through intense and sharp pain in one of the halves of the head, although bilateral migraines also occur. Symptoms of a nervous disease can be: drowsiness, irritability, which are replaced by acute pain head, nausea and vomiting, numbness of the extremities. Migraine can develop into more complex diseases of the nervous system. To date, there are no radical ways to treat migraine, and special medications are prescribed for the disease.
Myelitis- a disease that occurs with inflammation of the spinal cord and affects both white and gray matter. Symptoms of myelitis are: malaise, high fever, pain in the spine, back and legs, weakness, urination disorders. Diagnosis and subsequent treatment is prescribed by the doctor after passing the tests.
Stroke- this is the end point of the development of diseases of the nervous system, which implies a violation in the blood circulation of the brain. At the same time, blood flow to some parts of the brain decreases or completely stops getting. Experts indicate the presence of 2 types of stroke:
- Ischemic - occurs due to a violation of the passage of blood to the brain cells through the arteries;
- Hemorrhagic - appears due to hemorrhage in the brain.
Symptoms of a stroke are: the occurrence of pain in the head, followed by nausea and vomiting, palpitations, loss of consciousness, poor orientation in time and space, excessive sweating, a feeling of heat. Stroke is treated to prevent its recurrence and normalize blood flow to the brain. Hemorrhagic stroke requires surgical intervention.
One of the important issues of neurology are diseases of the peripheral nervous system. This kind of disease occurs in half of the patients who complain of nervous diseases. Depending on the affected area, diseases of the peripheral nervous system are:
- Radiculitis - diseases of the roots of the spinal cord;
- Plexitis - a violation in the work of the nerve plexuses;
- Ganglionitis - a disease associated with sensitive nerve nodes;
- Neuritis of the cranial and spinal nerves.

Neuropathy (neuritis) - nervous disease that occurs when the nerve becomes inflamed. There are neuritis of the facial nerve, small tibial and radial nerves. a clear sign such disease of the nervous system is the numbness of parts of the face, arms or legs. Most often it occurs from hypothermia of a person, the cause of the disease is a pinched nerve or its inflammation.
To prevent diseases of the peripheral nervous system, it is necessary to carefully monitor your health: do not overcool, avoid injuries, limit the effect of pesticides on the body and do not abuse smoking and alcohol.
Nervous and mental diseases. Diseases due to nerves
psychoses- a kind of nervous and mental illness that occurs when suffering a mental trauma. They can also appear after infectious diseases, overwork, insomnia and head injuries. Patients require hospitalization, special care and treatment with psychotropic drugs.
Epilepsy- diseases on the basis of nerves, which occurs due to changes in the brain. A sign of this mental illness is clouding of consciousness, convulsive (epileptic) seizures, foaming from the mouth. Treatment occurs with the help of drugs and special therapies.
A brain tumor- Availability mental disorder on the basis of the development of a tumor in the body. Patients who have such nervous and mental diseases suffer from excessive fatigue, pain in the head, impaired memory, incoherent speech, and loss of consciousness is possible. Patients require special permanent care, the treatment is neurosurgical.
progressive paralysis- a disease that manifests itself in the defeat of the pale spirochete of the brain. The initial stage of the disease has the following symptoms: exhaustion of the body, irritability, deterioration of memory and performance, impaired speech and progression of dementia. If progressive paralysis is started, then after a few years the disease leads to a state of insanity and subsequent death.
It's no secret that the nervous system is responsible for the work of the entire human body and the interconnection of all systems and organs. It performs very important functions, since it is able to unite the peripheral nervous system with the nerves extending from the spinal cord and brain, and the central nervous system, which consists of the spinal cord and brain. It is the nerve endings that provide sensitivity to all areas human body and motor activity. The cardiovascular system, as well as other organs, is inverted by a separate autonomic nervous system.
The nervous system consists of an extremely large number of branched unique subsystems. It is for this reason that diseases of the nervous system are so wide, and also have such a diverse number of pathologies with different etiologies and symptoms. Often, disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system irrevocably affect the activity of the rest internal systems and organs.
Classification of diseases of the nervous system
All diseases of the nervous system are divided into infectious, vascular, hereditary, traumatic pathologies, chronically progressive.
Vascular diseases are extremely dangerous and common. Very often they can provoke disability or death of the patient. This group includes disorders in the cerebral circulation of an acute nature (for example, strokes) and chronically current cerebrovascular insufficiency, which can cause changes in the brain. Such disorders can develop due to atherosclerosis or hypertension. If a person has disorders of the vascular disease of the nervous system, then this disease can manifest itself in him with vomiting, nausea, headaches, decreased sensitivity and impaired motor activity.
The disease can progress to a chronic form due to metabolic disorders, intoxication, the pathogenic effect of the infection and the complex structure of the nervous system. IN this group include diseases such as myasthenia gravis and sclerosis. As a rule, the disease proceeds for a very long time, and the lesions are systemic character. The signs of the disease increase gradually, as a result of which the viability of certain body systems decreases.
By heredity, diseases are chromosomal and genomic. Among the most common chromosomal diseases is Down's disease, while genomic pathologies most often affect the neuromuscular system. Among the characteristic disorders of dementia, one can distinguish such as disorders of the locomotor apparatus and the endocrine system, infantilism and dementia.
Traumatic injuries can occur due to bruising, trauma, compression of the brain, spinal or brain. These include: a concussion, which is accompanied by a headache, vomiting, memory loss, disorders of consciousness, nausea, decreased sensitivity.
Causes of diseases of the nervous system
To begin with, let's list all the infectious agents of diseases of the nervous system:
In addition to these pathogens, diseases can also be transmitted during pregnancy through the placental route (rubella, cytomegalovirus) or through the peripheral nervous system. For example, herpes, rabies virus, meningoencephalitis and acute poliomyelitis are transmitted this way.
Very common causes of diseases of the nervous system are chronic progressive diseases or heredity (Parkinson's disease, chorea, Alzheimer's disease), brain contusions, vascular disorders (inflammation, thrombosis or rupture), brain tumors, as well as their metastases.
The nervous system is also affected by an unbalanced diet, an insufficient amount or lack of vitamins, kidney, endocrine or heart diseases. Exposure to various chemicals can develop pathological processes, namely: poisons of plant and animal origin, ethyl alcohol, antidepressants, barbiturates, opiates. You can also get sick due to poisoning with anticancer drugs, antibiotics or heavy metals (thallium, manganese, bismuth, lead, arsenic, mercury).
Symptoms of diseases of the nervous system
Symptoms of the disease can manifest themselves in different ways, but often in the form of movement disorders. The patient may develop paresis (decreased muscle strength) or paralysis, inability to move quickly, involuntary rapid movements (chorea), tremors. Very often, pathological postures (dystonia) may appear. There are speech and coordination disorders, shudders, tics, involuntary contractions of some muscle groups. Tactile sensitivity may also be impaired.
Other important symptoms of diseases of the nervous system are pain in the neck and back, legs and arms, migraine (headaches). Very often, pathological changes can affect other types of sensitivity: vision, taste, smell.
Diseases can also be manifested by epileptic seizures, disorders of consciousness and sleep, mentality, behavior, and mental activity.
How to diagnose diseases of the nervous system?
To diagnose diseases, it is necessary to conduct a neurological examination of the patient. During the examination, his reflexes, sensitivity, intelligence, consciousness, orientation in time and space are analyzed. Sometimes diseases are detected on the basis of clinical indicators, but, as a rule, additional studies are necessary to make a correct diagnosis. For this, computed tomography of the brain is performed, which allows detecting hemorrhages, neoplasms and other foci of the disease. Magnetic resonance imaging gives a clearer picture, and ultrasound and angiography can reveal vascular disorders.
To diagnose diseases, electroencephalography or radiography, and lumbar puncture are also used. It is also necessary to highlight such methods as a blood test and a biopsy.
Drug treatment of diseases of the nervous system
The symptoms and type of diseases of the nervous system will determine what treatment the doctor will prescribe, as well as the use of intensive care in the hospital.
In order to avoid diseases of the nervous system, it is necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle, without the use of drugs and alcohol, not to overwork, avoid stress, eat well and diagnose and treat any infection in time. It is worth remembering that if any alarming symptoms appear, it is necessary to consult a doctor.
VIDEO
How to treat diseases of the nervous system with traditional medicine?
The benefits of buckwheat in the treatment of trigeminal nerve disease
In order to cure such a common disease as inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, it is recommended to use buckwheat. To do this, you need to warm it in a pan and put it in a cotton bag or sock. Such a kind of heating pad should be applied to the sore spot and kept until the buckwheat has completely cooled down. Such actions should be performed twice or thrice a day.
It is also very useful to rinse your mouth with infusion of chamomile. One teaspoon should be poured with a glass of boiling water. Such tea should be kept in the mouth as long as possible. The procedure is allowed to be carried out four times a day.
Hops in the treatment of the nervous system
Oddly enough, but it is ordinary hops that are considered very effective tool for the treatment of diseases of the nervous system. With it, you can get rid of insomnia and relieve irritability and nervousness. In order to prepare the remedy, you need to dry the hop cones and brew tea from them. We take a couple of cones, fill them with one glass of boiling water and leave for ten or fifteen minutes. Then we add honey to the tea, which makes it less bitter. It is advisable to drink two glasses of such tea per day, but no more.
Remember that the nervous system is greatly influenced by the diet. Therefore, it is worth taking food rich in lecithin and vitamin B. It is very useful to eat fatty fish, fish oil, liver, yeast, vegetable oil, dairy products, buckwheat, legumes, honey and eggs. But with all this, do not forget about the correct daily routine, eat a balanced diet, go to bed at the same time, walk a lot in the fresh air and do morning exercises.
Treatment of the nervous system with geranium and lemon balm
For the treatment of inflammation of the occipital nerve, you can use tea from lemon balm and orange peel. All ingredients must be dry, chopped and thoroughly mixed. We take one tablespoon of raw materials, pour boiling water and insist 10 minutes. Then we mix the strained tea with a teaspoon of valerian tincture. The course of treatment is one month. The infusion should be taken every day, 250 ml in two or three divided doses.
Ordinary indoor geranium also has healing properties, because it shoots great headache. To do this, you need to attach a few plucked leaves of the plant to the sore spot, cover with linen cloth and bandage with a woolen scarf. Leaves should be changed every two hours.
one of the many signs of diseases of the nervous system are also convulsions. For treatment, it is necessary to use infusions of horsetail or celery. The course of treatment should be seven days.
We treat the nervous system with valerian
For more than a century, valerian-based preparations have been prepared for the treatment of diseases of the nervous system. To prepare one of them, you need to take the leaves of shamrock and peppermint and combine them with valerian root and hop cones in a ratio of 2:2:1:1. Grind and mix the crushed ingredients, then pour one glass of boiling water and evaporate for 15 minutes in a water bath under a lid. After that, we insist the broth for 45 minutes and filter. We add boiled water to the resulting mixture, bringing it to the original volume. The decoction should be taken twice a day after meals, a quarter cup.
A decoction of valerian root is great for taking baths before bed. Such baths perfectly soothe and normalize sleep. We take half a kilogram of valerian roots, pour four liters of water and boil for an hour and a half. After that, we insist the broth for 12 hours and filter. Valerian can be replaced with cumin, pine needles and cones, lavender flowers and stems.









